SEM vs SEO is a crucial topic for businesses that want to stand out in search engine results. By boosting your visibility when users type in relevant keywords, you can direct traffic to your site, increase brand recognition, and ultimately secure more conversions or sales. Yet the question remains: which is better for your goals, SEM vs SEO—or is a combination of both the ideal solution?
This article explores the differences and synergies between SEM vs SEO to help you make a well-informed decision. You’ll learn how each strategy works, what they cost, how quickly you can expect results, and how to measure success. By the end, you should have a clear sense of which approach—SEM vs SEO—best aligns with your business objectives, resources, and timelines.
SEM vs SEO: Understanding the Terminology
Search engine marketing (SEM) generally refers to tactics designed to improve a website’s visibility in search engine results. In practice, SEM can encompass both paid and organic methods. However, most discussions use SEM to describe paid advertising on platforms like Google Ads, while “SEO” references the process of optimizing your site to rank higher in the organic (unpaid) listings.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
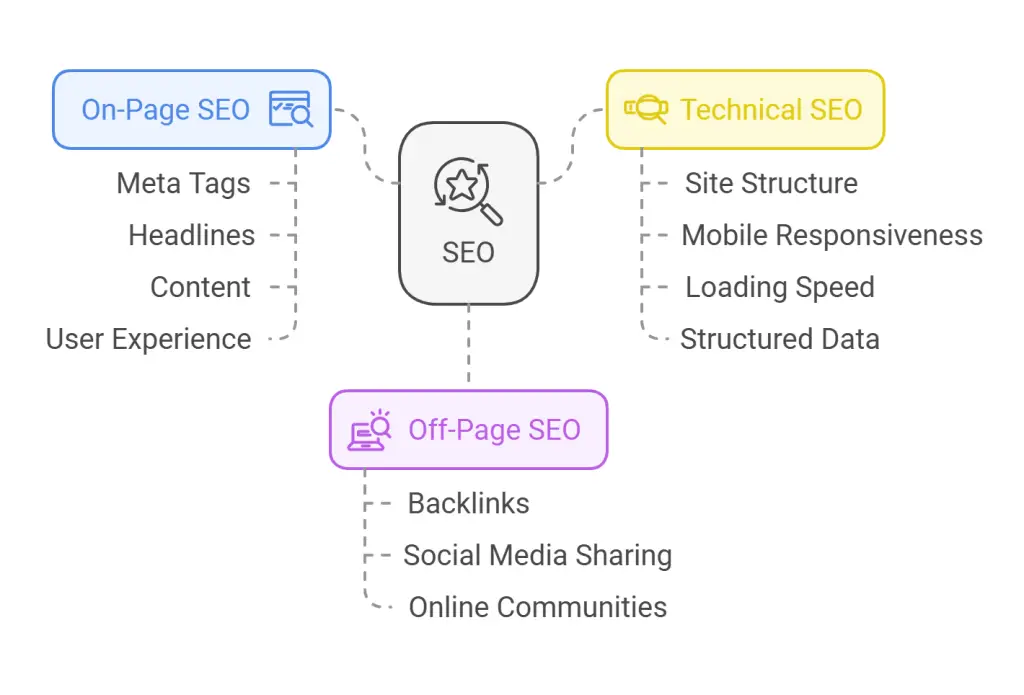
SEO focuses on boosting the organic position of your web pages in search results. The main areas of SEO include:
• On-Page SEO: Optimizing meta tags, headlines, content, and user experience (UX) to align with both user intent and search engine algorithms.
• Off-Page SEO: Building high-quality backlinks from credible websites, encouraging social media sharing, and participating in relevant online communities.
• Technical SEO: Ensuring your site structure, mobile responsiveness, loading speed, and structured data adhere to best practices so that search engines can crawl and index content efficiently.
Paid Search (Often Called SEM)
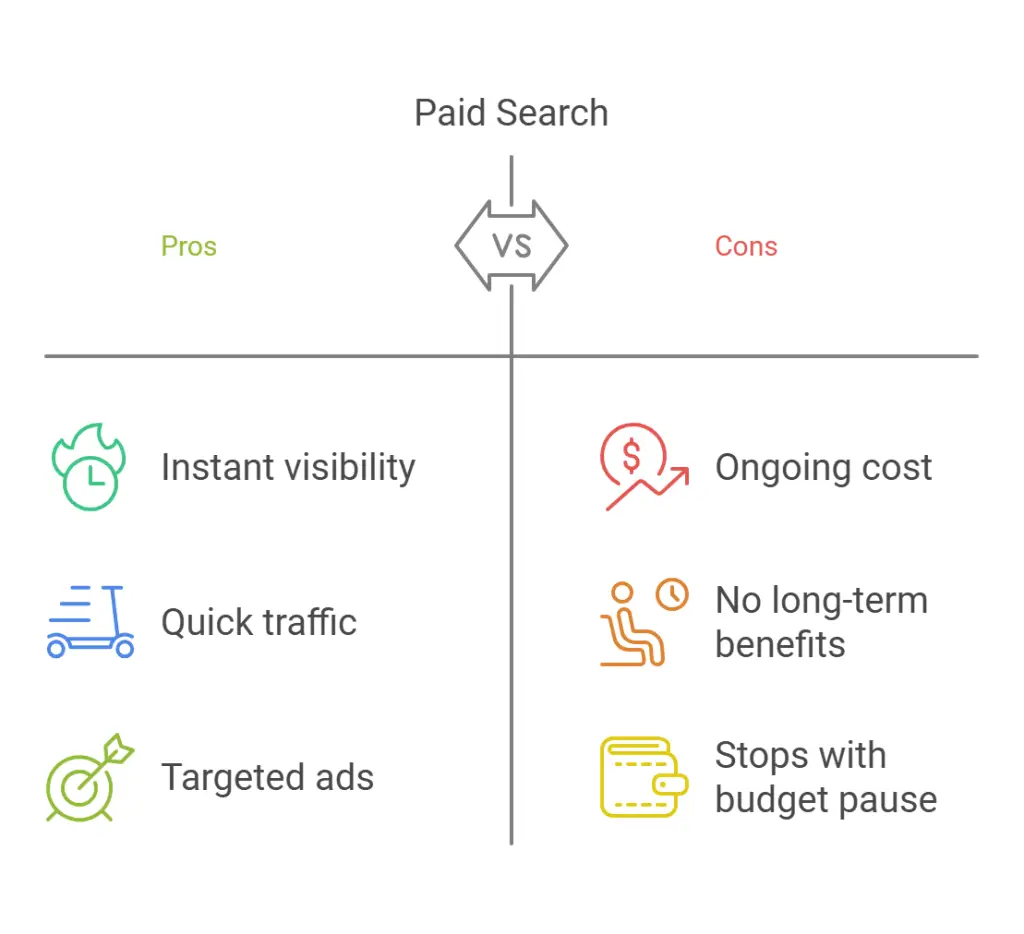
Under the SEM umbrella, paid search campaigns (commonly called PPC advertising) let you bid on specific keywords. Your ads can appear at the top of search engine results pages, giving your business near-instant visibility. You pay each time someone clicks on your ad. While this approach can generate traffic quickly, it only works as long as you’re funding it. Unlike SEO, which can build a long-lasting foundation of organic traffic, paid ads stop showing the moment you pause your budget.
Why Visibility Matters in SEM vs SEO
Most online interactions start with a query typed into a search engine. If your site doesn’t appear when users look for relevant terms, you might lose them to competitors. Whether through organic SEO strategies or paid SEM ads, search visibility captures targeted visitors who are already showing interest in the solution or service you offer. In the SEM vs SEO debate, both can contribute significantly to:
• Brand Awareness: Being visible in search results helps build credibility, as users perceive highly ranked businesses as more reputable.
• Qualified Traffic: People arriving from specific queries are often closer to making a purchase decision or seeking more detailed information.
• Revenue Growth: By aligning your site with relevant searches, you create opportunities for sign-ups, purchases, and other high-value conversions.
Key Differences in SEM vs SEO
Cost Structure
• SEM (Paid Search): Requires a budget to pay for each click. The cost per click (CPC) depends largely on keyword competitiveness and quality scores. If you’re in a crowded niche, costs may be higher.
• SEO (Organic): You invest in tasks like content creation, keyword research, link-building, and technical optimizations. While there’s no direct fee per click, achieving results might require substantial time or outsourced expertise.
Speed and Time to Results
• SEM vs SEO shows a clear difference in how fast you see outcomes. Paid ads can start bringing traffic almost immediately once you set up the campaign.
• SEO typically needs weeks—or months—of consistent effort before you notice major gains in ranking and traffic.
Long-Term vs Short-Term Sustainability
• SEM provides immediate visibility, but once you stop paying for ads, your traffic drops off.
• SEO can generate ongoing traffic even if you scale back your efforts later, though you still need some maintenance to stay competitive and adapt to algorithm changes.
User Trust and Click-Through Rates
• Many searchers place greater trust in organic results, perceiving them as more authoritative or unbiased.
• Paid ads often sit at the top of the page and can attract clicks from users who see them first, but some people intentionally skip ads and scroll down to organic listings.
Diving Deeper into SEO in the Context of SEM vs SEO
On-Page Optimization
For SEO, on-page factors are often the priority:
• Title Tags and Meta Descriptions: Craft compelling tags with your primary keywords, including variations of your topic if relevant to your content.
• Header Tags (H1, H2, H3): Use structured headings to guide readers and emphasize critical points.
• Keyword Placement: Incorporate focus keywords naturally, ensuring the content flows well.
• Content Quality: The more helpful and in-depth your content, the longer users stay on your page, signaling a positive user experience to search engines.
Off-Page SEO and Backlinks
Search engines gauge credibility by seeing who links to your site. Quality backlinks from well-regarded websites can improve your domain authority.
• Earning Links: Create in-depth guides, research, or thought leadership pieces that others want to reference.
• Outreach: Contact site owners or influencers in your industry to share your content, potentially gaining a link or mention.
• Social Signals: While not a direct ranking factor in the same way as backlinks, social sharing can expose your content to more readers who may then link to it.
Technical SEO Factors
Technical improvements ensure search engines can index your site without obstacles:
• Site Speed: Slow-loading pages frustrate users, leading to higher bounce rates.
• Mobile Responsiveness: More searches occur on phones, so a mobile-friendly design is essential.
• Structured Data: This helps search engines understand your content context and may enable rich snippets in results.

Exploring SEM and Paid Campaigns
How Paid Search Works
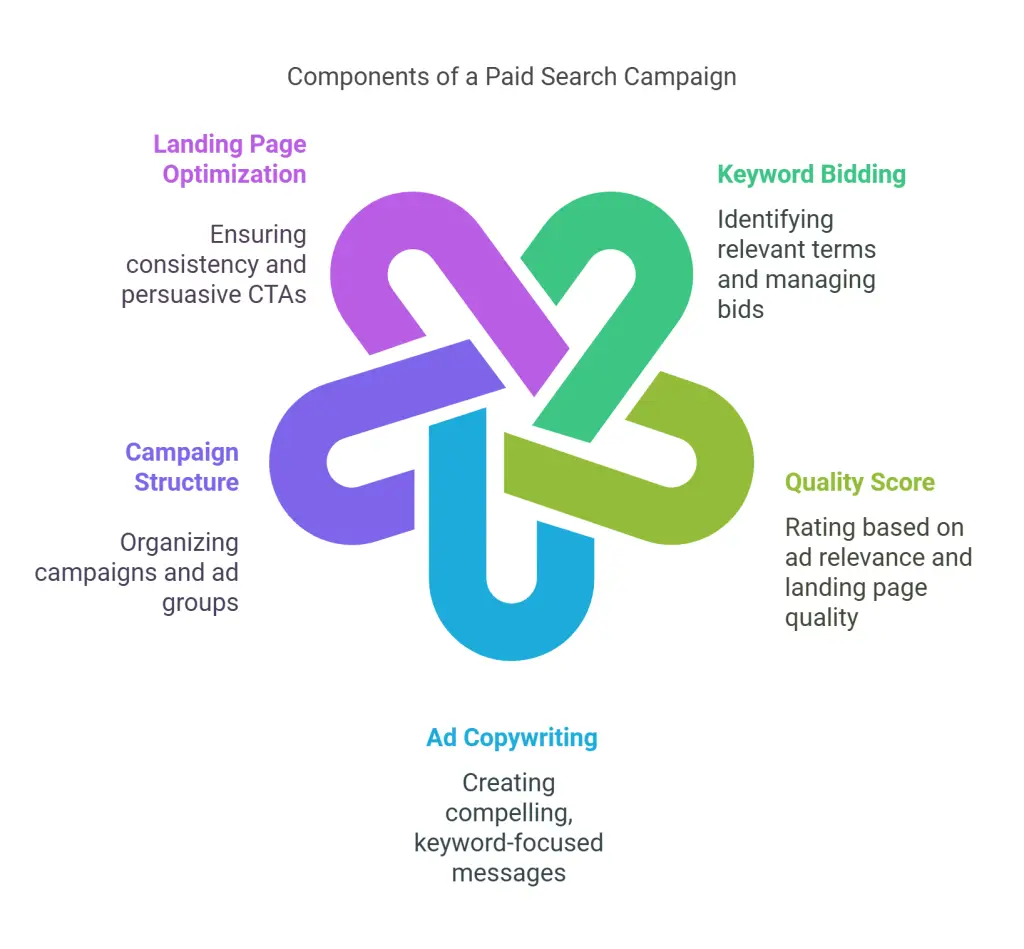
When evaluating SEM vs SEO, SEM can give you near-instant traffic. A typical paid search setup includes:
• Keyword Bidding: Identify terms relevant to your products or services. The amount you bid affects where and how often your ads appear.
• Quality Score: A rating from search engines based on your ad’s relevance, click-through rate (CTR), and landing page quality. A high-quality score can reduce your cost per click.
• Ad Copywriting: Compelling, keyword-focused messaging encourages users to click.
Campaign Structures and Ad Groups
Organizing your campaigns effectively makes them easier to manage and optimize:
• Campaign: A broad category or marketing goal (e.g., “Men’s Shoes”).
• Ad Groups: Subdivisions within a campaign, each targeting closely related keywords (“Running Shoes,” “Dress Shoes”).
• Ad Variations: Different headlines or descriptions that you test against each other to find the highest-performing copy.
Landing Page Optimization
Your ad’s promise must match the landing page content:
• Consistency: The headline on the landing page should reflect the wording of your ad.
• Clear Value Proposition: Explain why visitors should choose your offer.
• Persuasive CTAs (Calls to Action): Make it straightforward to sign up, purchase, or contact you.
• User Experience: Fast load times, appealing design, and easy navigation keep people engaged.
When to Choose SEM vs SEO—or Both
Business Goals
• If you’re running a short-term promotion or a product launch and need fast leads, SEM usually works better.
• If you aim to build a reliable, cost-effective traffic source that grows over time, SEO fits well.
• Many businesses do both: deploy SEM for immediate exposure while laying the foundation for robust, long-term SEO traffic.
Budget Constraints
• Smaller budgets might limit your paid ad reach, especially in high-CPC markets. In that case, focusing on SEO can yield more sustainable results.
• If you have a flexible budget, strategic paid campaigns can quickly test what keywords convert best, then channel that data into your SEO efforts.
Competitive Landscape
• In a niche with low to moderate competition, you may rank relatively quickly with a proper SEO plan.
• If you’re in a fiercely contested market, SEM offers a way to level the playing field in the short term, though you’ll still need SEO for long-term staying power.
Combining SEM vs SEO
Rather than viewing SEM vs SEO as mutually exclusive, many companies integrate both. Paid ads can bridge the gap while your organic rankings improve. You can also retarget users who clicked on paid ads, serving them relevant reminders to return. Over time, successful SEO efforts can reduce your dependence on paid ads, saving money and building brand trust.
Expected Time Frames in SEM vs SEO
SEO Timelines
• New Sites: Plan on at least three to six months before you see meaningful results.
• Established Sites: Could improve faster if you already have some authority and quality content.
• Ongoing Updates: Even after achieving solid rankings, stay consistent with content creation and technical upkeep.
SEM Timelines
• Immediate Results: Campaigns can start driving clicks and conversions almost immediately.
• Continuous Optimization: You’ll need to refine bids, ad copy, and targeting to maintain or improve your ROI over time.

Cost and ROI in SEM vs SEO
SEO Expenses
• You may pay for tools like keyword research platforms or analytics software, plus the time cost of content creation and link outreach.
• ROI can be high once your content ranks well and continues drawing traffic at minimal incremental cost.
SEM Expenses
• You pay per click, which can add up quickly if you target highly competitive terms.
• When optimized carefully, you might achieve a strong return on ad spend (ROAS). Sloppy campaigns, however, can burn through budgets with little to show.
Scaling Strategies in SEM vs SEO
Scaling SEO
• After addressing basic on-page factors, expand your content portfolio to target additional relevant keywords.
• Invest in link-building efforts, potentially hiring a PR or outreach specialist to earn high-quality backlinks.
• Improve internal linking structures, site navigation, and user experience to accommodate growing traffic.
Scaling SEM
• Introduce new campaigns for different products, services, or locations.
• Diversify your ad formats by including display, shopping, video, or remarketing campaigns.
• Review performance metrics often to pause low-performing ads and reallocate the budget to top performers.

Tactical Tips to Excel in SEM vs SEO
Keyword Research
• Identify your “SEM vs SEO” focus keyword if your content covers that debate, as well as other key terms related to your products and services.
• Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to see search volumes and competition levels.
High-Quality Content
• For SEO, produce thoroughly researched posts that align with user intent. This may mean tutorial guides, how-to videos, or even infographics.
• For SEM, ensure your landing pages fulfill the promises you make in ads and are optimized for conversions.
Performance Tracking
• SEO Metrics: Monitor organic traffic, keyword positions, domain authority, bounce rate, and dwell time.
• SEM Metrics: Focus on impressions, clicks, CTR, conversions, cost per conversion, and ROAS.
• Regularly review these metrics and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Staying Current
• SEO evolves due to frequent search engine algorithm updates. Follow reliable marketing blogs or official announcements to keep up.
• For SEM, ad platforms like Google Ads occasionally change how ads are displayed or how quality scores are calculated. Stay informed to optimize ad placements and costs.
Common Pitfalls in SEM vs SEO
SEO Pitfalls
• Keyword Stuffing: Overuse of your focus terms can hurt rankings and readability.
• Duplicate Content: Publishing similar content across multiple pages confuses search engines.
• Neglecting Technical Factors: Even great content won’t rank well if your site is slow or poorly structured.
SEM Pitfalls
• Irrelevant Ad Copy: Failing to address user intent results in low-quality scores and wasted spending.
• Poor Landing Pages: An ad might promise a big discount, but if the page doesn’t showcase it clearly, visitors bounce.
• Insufficient Testing: Running the same ad copy and strategy for months without analysis misses opportunities to refine and improve.

Sector-Specific Perspectives on SEM vs SEO
E-Commerce
• SEO: Product pages and category pages that rank well can consistently attract ready-to-buy customers.
• SEM: Seasonal sales like Black Friday can benefit from immediate boosts in visibility via paid ads, driving quick conversions.
Local Services
• SEO: Optimizing for local “near me” searches and maintaining a Google Business Profile draws consistent local leads.
• SEM: Running ads targeting urgent keywords like “emergency plumbing” can yield high-intent inquiries right when you need them.
Content-Focused Websites
• SEO: Publishing high-quality, in-depth articles attracts organic traffic seeking information.
• SEM: Paid ads can spotlight new content or special features, validating ideas quickly before investing in broader SEO efforts.
Forming a Balanced SEM vs SEO Strategy
Combining Strengths
• Use SEM data to discover your highest-converting keywords, then expand your SEO content around them.
• When an SEO article performs exceptionally well, push it further with paid ads during peak seasons for maximum exposure.
Adapting to Market Shifts
• Seasonal Fluctuations: Retailers might rely heavily on paid campaigns during holidays but shift to SEO-based efforts the rest of the year.
• Economic Changes: If budgets tighten, focusing on SEO helps ensure you’re not cut off from all traffic if paid campaigns are scaled back.
Expanding Internationally
• SEO: Localize content for each market, translating pages and ensuring region-specific keywords are targeted.
• SEM: Set up separate campaigns or accounts to handle different languages, currencies, and cultural nuances.

Roadmap for Implementation of SEM vs SEO
SEO Implementation Steps
- Technical Audit: Assess site speed, mobile readiness, crawlability, and indexability.
- Keyword Strategy: Identify relevant terms and incorporate them into your content plan.
- On-Page Optimization: Update titles, headers, and meta descriptions for clarity and keyword relevance.
- Content Creation: Generate articles, videos, or guides that deliver real value to your audience.
- Link-Building: Earn authoritative backlinks through outreach, networking, and high-quality resource creation.
- Track and Optimize: Monitor search rankings and user behavior; make changes based on new insights.
SEM Implementation Steps
- Set Up Advertising Accounts: Use Google Ads (and possibly Bing Ads) with proper billing and location targeting.
- Campaign Structuring: Group keywords logically into campaigns and ad groups.
- Ad Creation: Write compelling headlines and descriptions, highlighting your unique selling points.
- Landing Page Alignment: Ensure each ad points to a page that meets user expectations.
- Ongoing Analysis: Watch your clicks, conversions, and CTR. Optimize bids, ad text, and negative keywords.
- Expand and Refine: Explore display ads, remarketing, or video campaigns once you master the basics.
Measuring Success in SEM vs SEO
SEO Metrics
• Organic Traffic: Track visitors landing on your site from unpaid search results.
• Keyword Rankings: See where you stand for priority terms, including “SEM vs SEO” if that’s your focus.
• Engagement: Look at bounce rates, time on page, and pages viewed per session.
• Backlinks: See how many sites link to your content and whether they are high-authority sources.
SEM Metrics
• Impressions: How often your ad is shown to searchers.
• Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of impressions that result in a click.
• Conversions: The number of users who took a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form.
• Cost Per Conversion: How much you pay on average to secure each sale, sign-up, or other goal.
• Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): How much revenue each dollar of ad spend generates.
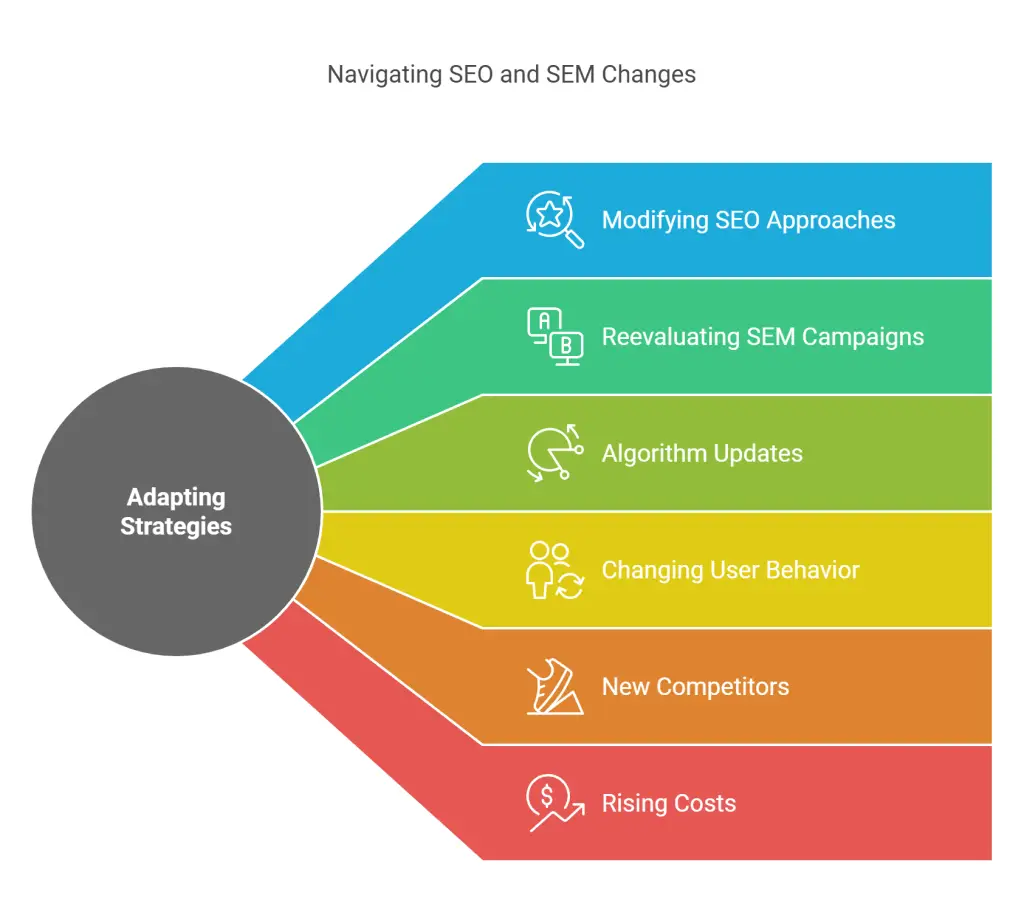
Adapting Over the Long Term
When to Modify Your SEO Approach
• Algorithm Updates: Watch for major shifts in how Google ranks content. Adjust your strategies accordingly.
• Changing User Behavior: If video content becomes more popular, you might pivot to producing more video-based material.
• New Competitors: Stay vigilant. Competitors might optimize aggressively, so keep track of your standing.
When to Reevaluate SEM Campaigns
• Rising Costs: If your cost per click grows too high, consider bidding on more specific, long-tail keywords or improving your quality score.
• Ad Fatigue: If the same ad runs too long, your audience might stop responding. Refresh your creative periodically.
• Market Changes: If consumer priorities shift, adapt your ad messaging and landing pages.
Bringing It Together: The SEM vs SEO Decision
SEM vs SEO is ultimately about balancing immediate visibility with long-term brand-building. If you need leads or sales right away, paid ads offer a direct path. Meanwhile, a commitment to SEO lays the groundwork for enduring, cost-effective traffic. Businesses willing to allocate resources to both often find they can achieve a faster return (via SEM) and simultaneously reduce dependency on paid traffic over time (through strong SEO foundations).
Conclusion
SEM vs SEO doesn’t have to be an either/or choice. Each method serves a distinct function in a well-rounded marketing plan. With SEM, you can quickly test keywords, gather audience insights, and drive immediate sales—ideal for short-term promotions or time-sensitive launches. With SEO, you slowly build a reputation as a reliable resource in your niche, capturing steady, organic traffic that doesn’t evaporate the moment you pause your advertising spend.
Whether you lean toward SEM, SEO, or both, keep your target audience’s needs at the forefront. Provide content, ads, and landing pages that speak to what they’re searching for. Continuously track your metrics and make improvements. In doing so, you’ll maximize visibility in search results and increase the odds of long-term success. By carefully weighing the pros and cons of SEM vs SEO, you’ll be well on your way to a more profitable and impactful online presence.
Frequency Asked Questions
What is the main difference between SEO and SEM?
SEO focuses on improving a website’s organic search rankings through optimization techniques, while SEM involves paid advertising to appear at the top of search engine results. SEO takes time to build lasting traffic, whereas SEM delivers immediate visibility but requires ongoing ad spend.
Which strategy is better for long-term results: SEO or SEM?
SEO is better for long-term results as it builds sustainable organic traffic through content, backlinks, and site optimizations. While SEM provides instant visibility, its effectiveness stops when the budget runs out, making SEO a more cost-effective long-term strategy.
How does SEM generate traffic compared to SEO?
SEM generates traffic through paid advertisements, where businesses bid on keywords and pay per click. In contrast, SEO attracts visitors organically by optimizing content, improving site structure, and building credibility with search engines over time.
Can SEO and SEM be used together?
Yes, combining SEO and SEM can maximize search visibility. SEM provides immediate traffic while SEO builds organic presence for long-term success. Many businesses use SEM for quick wins while working on SEO to establish a sustainable online presence.
How do you measure the success of SEO and SEM?
SEO success is measured through organic traffic growth, keyword rankings, and engagement metrics over time. SEM success is evaluated using click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, and return on investment (ROI), providing immediate insights into campaign performance.
Further Reading
Backlinko. “SEO Marketing Hub.” Accessed January 3, 2025. https://backlinko.com/seo-marketing-hub.
Enge, Eric, Stephan Spencer, and Jessie Stricchiola. The Art of SEO: Mastering Search Engine Optimization. 3rd ed. Sebastopol, CA: O’Reilly Media, 2015. Available at: https://www.amazon.com/dp/1491948965.
Google Ads Help. “About Google Ads.” Accessed January 3, 2025. https://support.google.com/google-ads/.
Google Search Central. “Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Starter Guide.” Accessed January 3, 2025. https://developers.google.com/search/docs/beginner/seo-starter-guide.
HubSpot. “The Ultimate Guide to SEO in 2023.” Accessed January 3, 2025. https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/seo.
Ledford, Jerri L. SEO: Search Engine Optimization Bible. Indianapolis: Wiley, 2009. Available at: https://www.amazon.com/dp/0470345021.
Moz. “Beginner’s Guide to SEO.” Accessed January 3, 2025. https://moz.com/beginners-guide-to-seo.
Neil Patel. “SEO Made Simple: A Step-by-Step Guide.” Accessed January 3, 2025. https://neilpatel.com/what-is-seo/.
Search Engine Journal. “SEO.” Accessed January 3, 2025. https://www.searchenginejournal.com/category/seo/.
Search Engine Land. “Search Engine Land Guide to SEO.” Accessed January 3, 2025. https://searchengineland.com/guide/seo.
SEMrush. “SEMrush Blog.” Accessed January 3, 2025. https://www.semrush.com/blog/







