Email marketing is a critical channel for businesses looking to cultivate a deeper relationship with their audience, drive consistent engagement, and boost revenue. While numerous communication platforms have emerged, email has stood the test of time as a powerful marketing medium. With most consumers checking their inboxes multiple times a day, email allows a direct line of contact that can lead to significant growth when used strategically. It remains one of the most cost-effective and reliable ways to promote products, share important content, offer special deals, and nurture relationships with prospects and customers.
This comprehensive guide dives into why email marketing still matters, the essential steps you should follow to build successful campaigns, and the best practices to sustain those campaigns over time. It outlines each step from defining your goals to testing and optimizing your efforts for maximum effectiveness. By the end, you will have a clear roadmap for planning, executing, and refining your email marketing strategies to meet your objectives and see concrete returns.
Why Email Marketing Matters
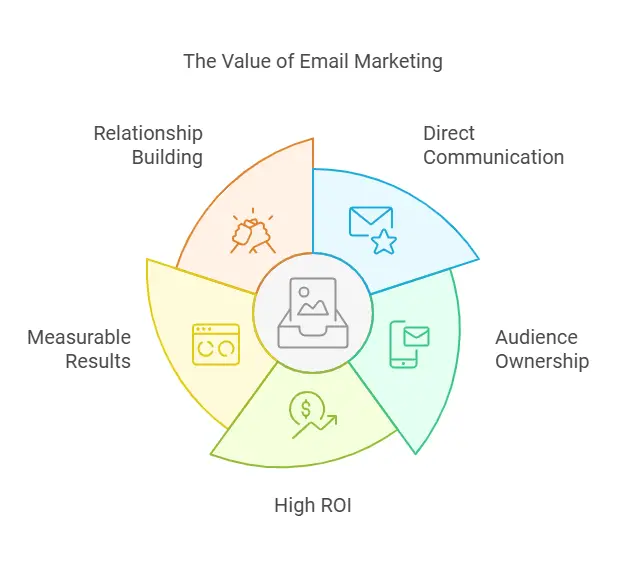
Many organizations wonder why they should invest in email marketing when social media platforms or search engine ads might seem more trendy. The truth is that email outperforms most channels in key metrics such as engagement, conversion rates, and returns on investment. Several compelling reasons underscore its continued relevance:
- Direct and Personalized Communication
Social media feeds are highly competitive. Algorithms determine which posts get shown to which audiences and paid ads can be costly. Email, on the other hand, is a direct channel where your message lands in a subscriber’s inbox. No intermediary is deciding whether or not the recipient will see it. This direct connection, combined with the ability to segment and personalize content, ensures that emails can be tailored to a subscriber’s interests, behaviors, or purchase history. - Ownership of Your Audience
On social media, you’re at the mercy of platform changes and policy shifts. If an algorithm changes, your reach might plummet overnight. With email lists, you own the contacts. Your marketing efforts are not dependent on a third party’s algorithm or regulation changes. The list you build is yours, making it a stable, long-term asset. - Superior Return on Investment
Research shows that for every $1 spent on email marketing, businesses often see an average return of $42. This ratio outperforms many other digital marketing tactics. Even smaller campaigns can be scaled without significant additional costs, allowing businesses to quickly ramp up efforts when they see positive results. - Trackable and Measurable
Email marketing platforms provide transparent data on open rates, click-through rates (CTR), bounce rates, and conversions. These metrics make it possible to gauge campaign success and fine-tune future campaigns based on real insights. - Relationship Building
Email can facilitate ongoing communication with leads and current customers. Through consistent newsletters and targeted messages, you can keep your audience informed about the latest developments, share valuable resources, and remind them of your offerings. Over time, these messages help foster trust, leading to improved loyalty and repeat purchases.
Understanding Email Marketing Fundamentals
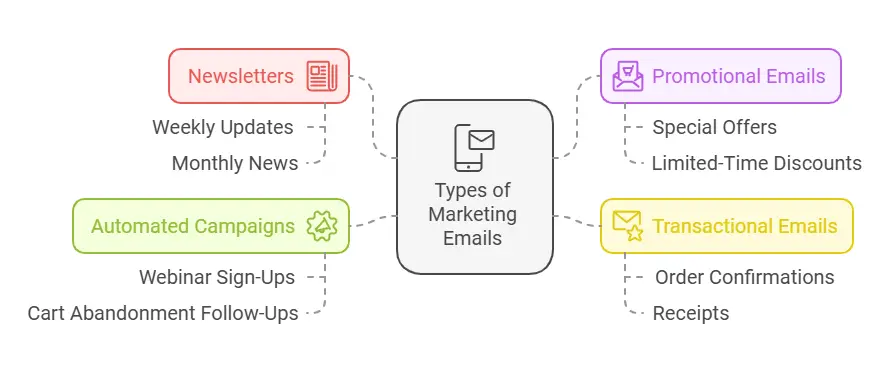
Email marketing is the process of sending promotional messages or newsletters to a group of subscribers who have opted in to hear from you. It aims to educate prospects, nurture leads, and boost sales while reinforcing brand identity. There are several common types of emails in marketing campaigns:
- Newsletters
These are regular communications—weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly—that keep subscribers updated on relevant news, blog posts, or product releases. Newsletters are essential for staying top-of-mind with your audience. - Promotional Emails
Promotional emails highlight a particular offer, discount, or sale on products or services. They are typically aimed at driving immediate conversions or sales. - Transactional Emails
These include confirmations, receipts, or follow-up emails triggered by a specific action taken by a user. For instance, after someone makes a purchase, you might send them a receipt along with a message that suggests related products. - Automated or Drip Campaigns
These emails follow a sequence triggered by specific user behaviors, such as signing up for a webinar, abandoning a cart, or downloading a lead magnet. Automation helps nurture leads by delivering timely and relevant messages without manual intervention.
Defining the Goals for Your Email Campaigns
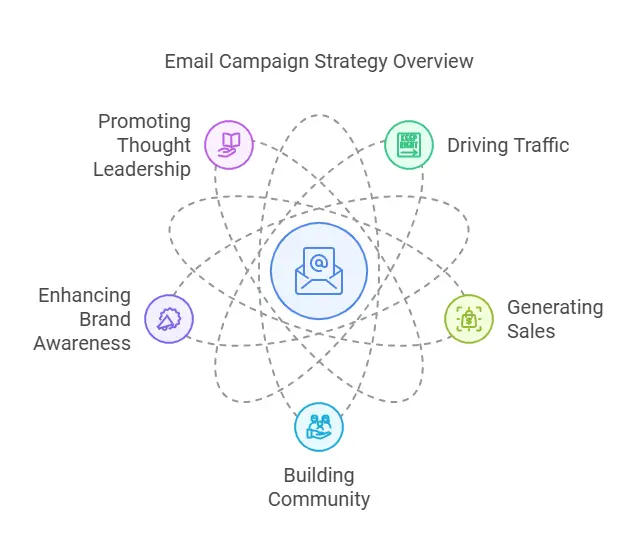
Every campaign should have a specific goal guiding its direction. Without a clear objective, it can be difficult to measure results or determine success. Possible goals include:
- Driving Traffic to a Website or Landing Page
If a primary business objective is to increase website visits, email can direct subscribers to new content, special events, or landing pages that expand on what was shared in the email. - Generating Sales
Whether you’re promoting a physical product, digital product, or service, email campaigns can drive direct purchases. You can send limited-time discount codes or highlight new product arrivals. - Building Community
Some marketers focus on nurturing a sense of belonging among subscribers. Campaigns might encourage members to contribute to a shared platform, attend events, or participate in community discussions. - Enhancing Brand Awareness
Periodic newsletters showcasing achievements, press mentions, or testimonials can help establish authority and credibility within a niche, leading to stronger brand recognition and trust. - Promoting Thought Leadership
For niche industries, emails that share exclusive insights, research, or long-form content can position your brand as a subject matter expert. Over time, recipients may look to you for the latest information and analyses in your field.
Building an Email List
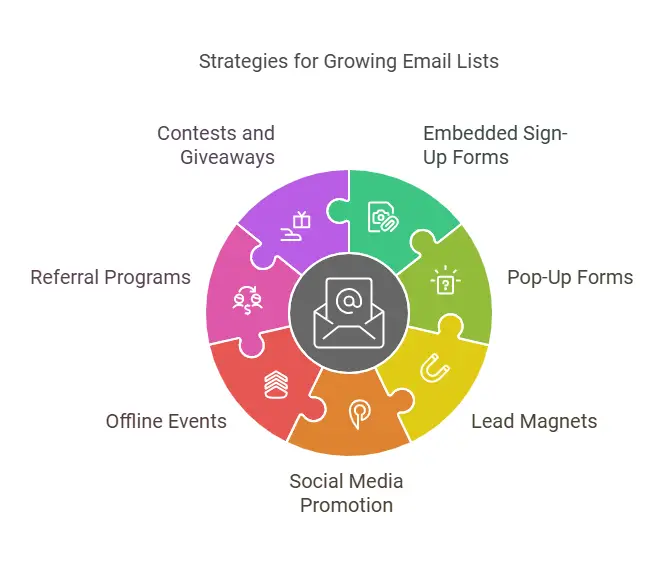
Your email list forms the foundation of every campaign. It’s crucial to attract the right subscribers—individuals who are genuinely interested in what you offer—rather than just building a large list with unqualified leads. Quality beats quantity, but there are several effective ways to bring in the right people:
- Embedded Sign-Up Forms
Place sign-up forms on your website homepage, blog sidebar, or dedicated landing pages. The form should be visually appealing, concise, and easy to locate. A headline that clearly states the value of signing up helps capture attention. - Pop-Up Forms and Slide-Ins
Targeted pop-ups or slide-in forms can be triggered by user behaviors, such as scrolling through a page or spending a certain amount of time on the website. While some visitors find pop-ups intrusive, well-timed pop-ups with an irresistible offer can be highly effective. - Lead Magnets
People are more likely to submit their email addresses if they receive something valuable in return. A lead magnet can be a free eBook, report, template, mini-course, webinar, or exclusive discount. The key is to ensure it aligns with the needs and interests of your ideal audience. - Social Media Promotion
Leverage your Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, or other social profiles to promote a sign-up page. You might tease the content of an upcoming newsletter or announce a free resource that visitors can access by joining your email list. - Offline Events and Networking
In-person events such as trade shows, meetups, or conferences offer opportunities to collect email addresses. Using tablet-based sign-up forms or providing QR codes that link to a subscription landing page can simplify the process. - Referral Programs
Word of mouth can be an effective method of expanding your list. Encourage current subscribers to share your newsletter with friends who have similar interests. Offer a small incentive (like a bonus guide or exclusive discount) if they successfully refer a friend who joins your list. - Contests and Giveaways
Hosting a contest can rapidly grow your list if the prize is relevant to your target audience. However, be cautious: irrelevant prizes may attract subscribers who are only there for the giveaway and will unsubscribe soon after. Ensure that your giveaway appeals to potential long-term subscribers.
Choosing the Right Email Marketing Platform
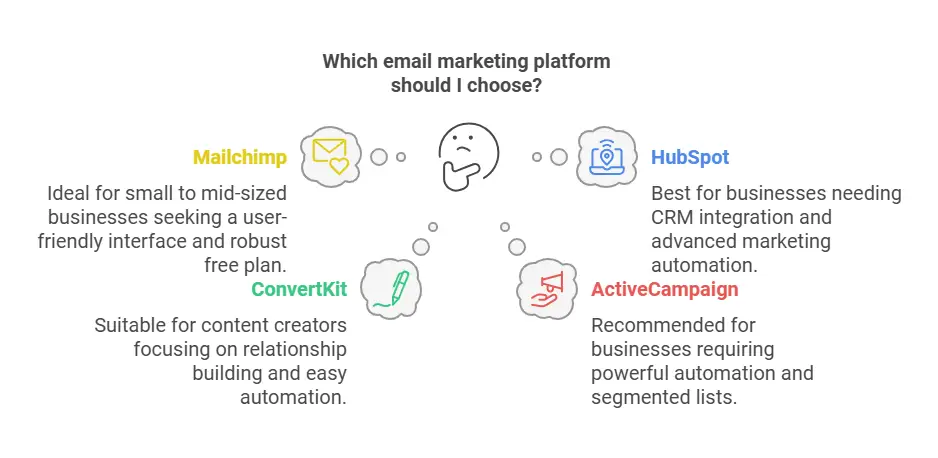
There are many email marketing tools available, each offering different features. Selecting the right platform depends on your business goals, the size of your list, and the level of sophistication you need. Some popular platforms include:
- Mailchimp
Known for its user-friendly interface and robust free plan, Mailchimp is a go-to choice for small to mid-sized businesses. It offers drag-and-drop email builders, basic segmentation tools, and analytics. - HubSpot
For businesses looking for more advanced features, HubSpot offers CRM integration, marketing automation, and advanced analytics in one ecosystem. It’s beneficial for companies planning to scale while keeping sales and marketing data in one place. - ConvertKit
ConvertKit caters to content creators and small businesses focused on building relationships. Its automation features are easy to set up, and its simple interface makes it quick to implement complex journeys, like nurturing sequences for an online course launch. - ActiveCampaign
This platform is known for its powerful automation features and extensive capabilities for creating and managing segmented lists. It’s often recommended for businesses that need advanced customer journeys. - GetResponse
A versatile platform with landing page builders, templates, and automation workflows, GetResponse aims to streamline the creation of sales funnels. It’s beneficial for those looking to integrate webinars, eCommerce, and email marketing.
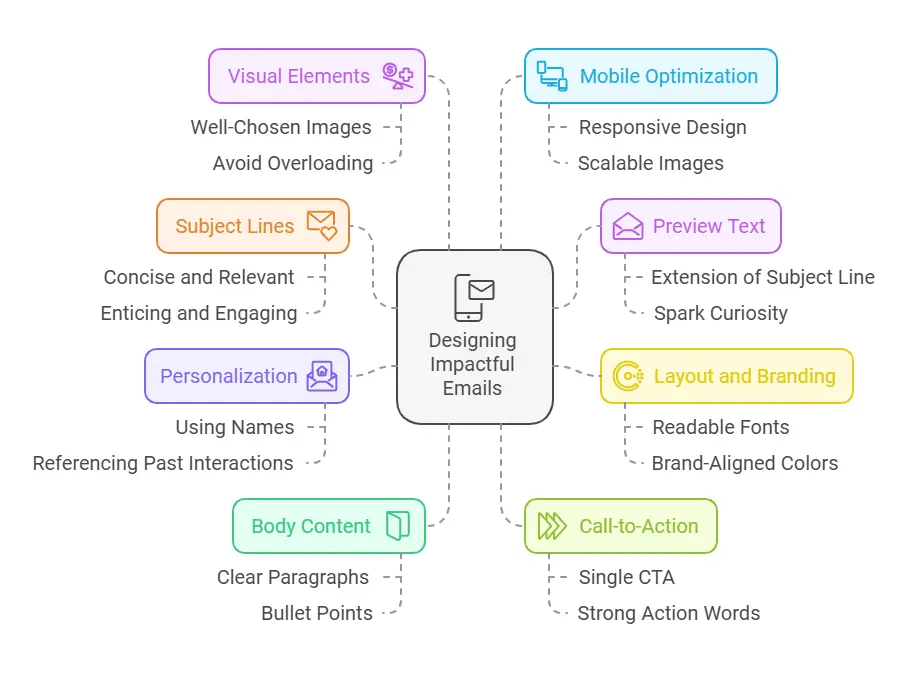
Designing Impactful Emails
The design and structure of your emails play a pivotal role in capturing attention and spurring action. Here are vital elements to keep in mind:
- Subject Lines
The subject line is often the deciding factor in whether an email is opened or ignored. It should be concise, relevant, and enticing. Some strategies include using numbers, asking a question, or offering a benefit directly. Avoid using spammy terms or excessive punctuation. - Preview Text
Preview text, visible next to or below the subject line in most inboxes, provides a teaser for your email’s content. Treat it like an extension of your subject line and ensure it flows cohesively to spark curiosity. - Layout and Branding
A clean layout with readable fonts and brand-aligned colors fosters a recognizable and professional appearance. Maintain consistency across all campaigns so subscribers can immediately identify your emails as coming from you. - Personalization
Using the recipient’s name in the greeting or subject line can boost open and click-through rates. Beyond names, personalization can involve referencing previous purchases or browsing behaviors. This tactic makes the email more relevant to each subscriber. - Body Content
Write in clear, concise paragraphs. Use bullet points, subheadings, or short sentences to break up text and improve readability. Avoid long blocks of text that can overwhelm you. Presenting content in a “scannable” format is essential, especially since many subscribers glance at emails while on the go. - Call-to-Action (CTA)
Include a single, clear CTA that aligns with your campaign goal. Too many CTAs can confuse subscribers, reducing overall clicks. Use strong action words: “Buy Now,” “Get Your Free Copy,” or “Start Your Trial.” - Visual Elements
Well-chosen images or graphics can help illustrate a point or draw attention, but they should never overshadow the message. Image-heavy emails can also trigger spam filters or load slowly on mobile devices. Strike a balance: one or two compelling visuals can be enough. - Mobile Optimization
An increasing percentage of users open emails on smartphones or tablets. Make sure images scale properly, text remains readable, and clickable elements are finger-friendly. Most email marketing platforms offer preview modes and responsive templates.
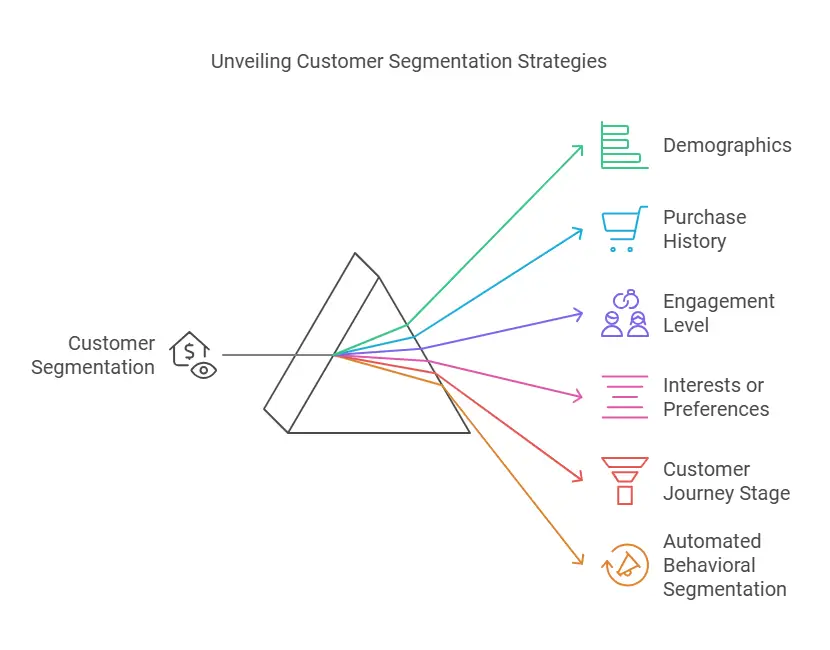
Segmenting Your Audience
Segmentation is the practice of dividing your subscribers into different groups based on shared attributes or behaviors. Sending a single, generic email to your entire list is easy, but segmentation often leads to better engagement because you’re offering more relevant content. Common segmentation criteria include:
- Demographics
Segment by age, gender, location, or other demographic information. This works well for businesses with region-specific offers or content. - Purchase History
Separating customers who have bought multiple times from those who have never purchased lets you send more relevant recommendations or incentives. - Engagement Level
Identify active subscribers who consistently open emails and click on links, as well as inactive ones who rarely do so. You can then target re-engagement campaigns at inactive subscribers while rewarding active ones with exclusive offers. - Interests or Preferences
You can learn about subscribers’ interests through surveys, sign-up forms, or tracked browsing behaviors. Sending specialized content aligned with topics they care about can significantly boost open rates. - Customer Journey Stage
Stage-based segmentation focuses on whether a subscriber is a new lead, in the decision-making phase, or a returning customer. New leads might get a welcome sequence while returning customers receive loyalty-driven messages or upsell offers. - Automated Behavioral Segmentation
Some platforms track how subscribers interact with emails or websites. If someone clicks on a certain product category repeatedly, they can be automatically placed into a segment interested in that category.
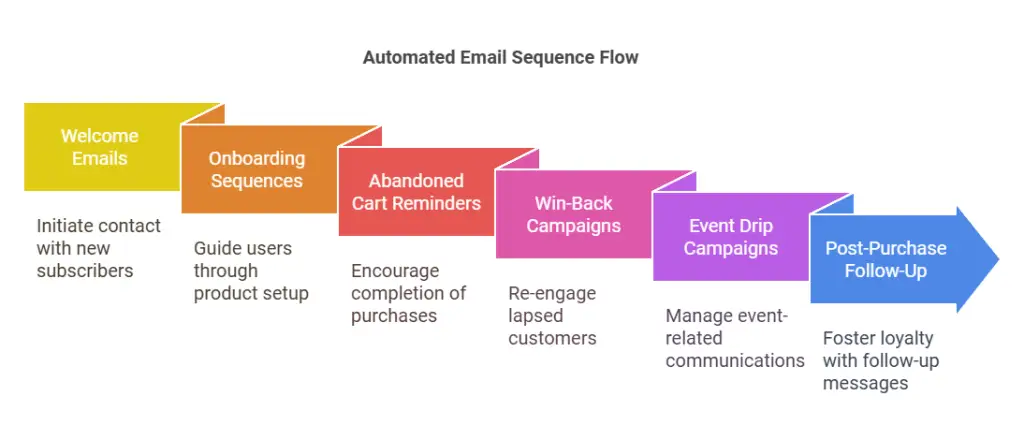
Implementing Automation
Automation ensures your audience receives timely messages without manual intervention for each phase or activity. Common automated sequences include:
- Welcome Emails
When someone joins your list, send an automated welcome email to greet them. This is your chance to make a positive first impression, deliver any promised lead magnet, and introduce brand values or popular products. - Onboarding Sequences
For more complex products or services, an onboarding sequence guides new customers through the initial steps. This can include tutorials, tips, and best practices to encourage them to fully use what they’ve purchased or signed up for. - Abandoned Cart Reminders
Online retailers lose potential revenue when customers add items to a cart but fail to complete checkout. Automated reminders often recover these lost sales by prompting the user with a direct link to resume shopping. - Win-Back Campaigns
Target lapsed subscribers or customers with a message intended to rekindle their interest. This might include an exclusive discount or an invitation to check out your latest offerings. - Event Drip Campaigns
If you’re hosting a webinar or in-person event, a drip series can handle everything from the initial registration confirmation to reminders leading up to the event, plus follow-up messages afterward. - Post-Purchase Follow-Up
After someone buys, you can send them a thank-you message, a request for feedback, or suggestions for related products. This sequence encourages additional sales and fosters brand loyalty.
Testing and Optimization
Launching a campaign is only the beginning. Continuous testing and refinement are essential. There are many elements you can experiment with:
- Subject Line Testing
Try different lengths, tones, or angles to see which subject lines lead to the highest open rates. Consider adding emojis or personalization, but keep a close watch on how it affects results. - A/B Testing Email Designs
Change one variable at a time, such as the main image, CTA placement, or color scheme. Identify what resonates best with your audience and systematically improve your emails. - Send Time Optimization
Different segments may have varying preferences on when they read email. Test sending times during mornings, afternoons, evenings, and different days of the week to find the best engagement patterns. - Frequency
Striking the right balance between staying relevant and overwhelming subscribers is tricky. Some audiences prefer frequent updates, while others respond better to a less frequent schedule. Gauge unsubscribe rates and engagement to guide your frequency decisions. - Personalization Testing
Try different approaches, such as including the subscriber’s name in the subject line, referencing their specific interests, or recommending products based on past purchases. Monitor which version sparks more interest and clicks. - Content Format
Experiment with different layouts, from shorter text-based emails to more elaborate, image-driven designs. Consider whether adding a short video clip or GIF increases engagement. - Landing Page Continuity
When subscribers click a CTA, ensure that the landing page they see matches the design and message of the email. A mismatch can increase bounce rates. Occasionally, test variants of the landing page to see which version yields better conversions.
Best Practices for Long-Term Success
Sustainable email marketing requires ongoing attention to detail. Incorporate these best practices to maintain a healthy list and consistent results:
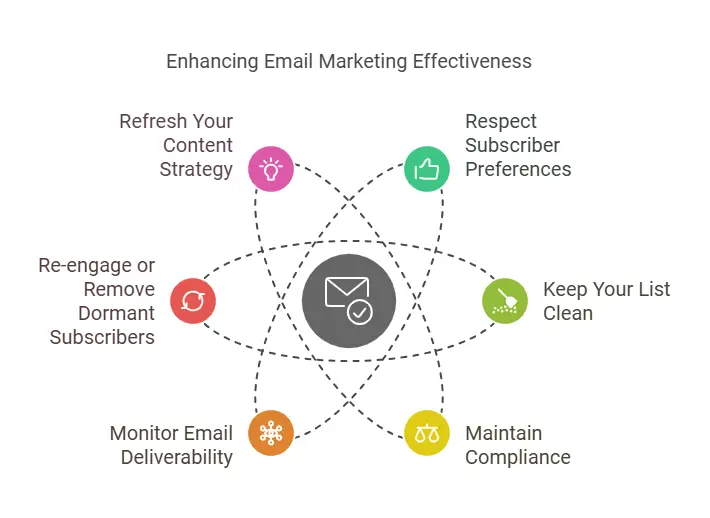
- Respect Subscriber Preferences
Allow subscribers to manage their preferences, such as how often they receive emails or what type of content they’d like. This approach reduces unsubscribes and spam complaints. - Keep Your List Clean
Regularly remove invalid or bounced addresses, and consider pruning inactive subscribers. A smaller but more engaged list can be more effective than a massive list of uninterested contacts. - Maintain Compliance
Regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CAN-SPAM (Controlling the Assault of Non-Solicited Pornography and Marketing) govern how marketers collect and use subscriber data. Always include an unsubscribe link, clearly identify who you are, and obtain explicit consent for marketing communications. - Monitor Email Deliverability
A high bounce rate or frequent spam complaints can hurt your sender’s reputation. Consistently track email deliverability metrics to ensure your messages are making it into inboxes. - Re-engage or Remove Dormant Subscribers
An occasional campaign aimed at subscribers who haven’t opened or clicked recently can bring them back if they’re still interested. If they remain disengaged, removing them helps maintain a healthy deliverability rate. - Refresh Your Content Strategy
Stagnant content can lead to audience fatigue. Occasionally adjust your tone, test new topics, or introduce fresh elements like interviews, tutorials, or user-generated content.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Some pitfalls can harm your campaign performance or even get your emails flagged as spam:
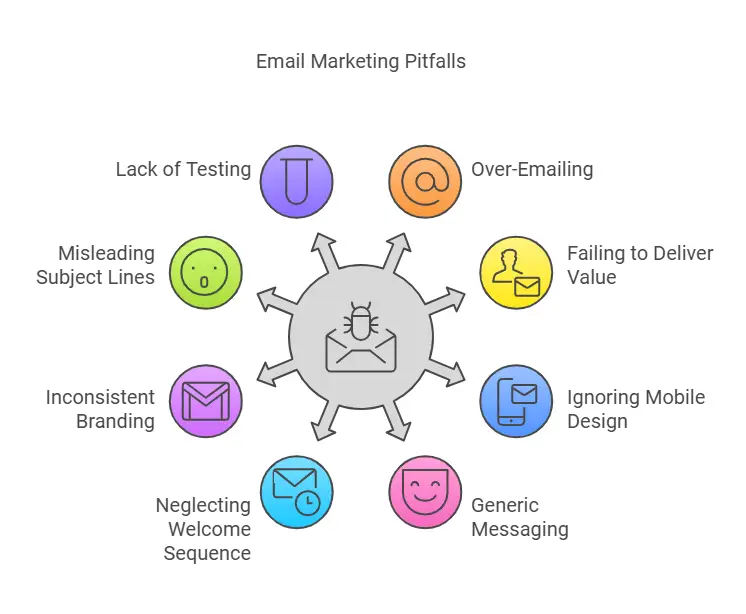
- Over-Emailing
Sending too frequently or with aggressive sales tactics can turn off your audience. Watch unsubscribe and spam complaint rates for red flags. - Failing to Deliver Value
If your emails read like constant sales pitches with no educational or entertaining content, recipients may lose interest. Aim for a balance of value-added content and promotions. - Ignoring Mobile-Friendly Design
With so many people reading email on phones, ignoring mobile optimization results in awkward layouts, tiny text, or inaccessible CTAs. This can severely dampen response rates. - Generic, Non-Segmented Messaging
If subscribers receive irrelevant content, they’re likely to unsubscribe or ignore your emails. Segmentation and personalization are crucial. - Neglecting the Welcome Sequence
When someone subscribes, they’re most receptive to hearing from you at that moment. Missing the opportunity to send an immediate welcome or lead magnet can reduce future engagement. - Inconsistent Branding
Erratic design choices or changing styles in every email can confuse subscribers about your brand identity. Consistency aids recognition and trust. - Misleading Subject Lines
Tricking people into opening an email only leads to higher unsubscribe and spam complaint rates. Always ensure the subject line aligns with the content inside. - Lack of Testing
Assuming you know what your audience prefers without running tests can lead to missed opportunities. Testing helps you find incremental ways to boost performance.
Measuring Success with Analytics
Measuring results is critical for continuous improvement. Here are important metrics to track:
- Open Rate
This indicates how many subscribers opened your email. A low open rate can signal weak subject lines, poor send times, or a lack of interest. - Click-Through Rate (CTR)
CTR shows how many recipients clicked on a link in your email. It measures how effective your message and CTA are. - Conversion Rate
A conversion is when a recipient takes a desired action, like making a purchase or filling out a form. Tracking conversions connects your email campaigns to bottom-line results. - Bounce Rate
The bounce rate measures how many emails were undeliverable. A high bounce rate might indicate an outdated list or issues with email formatting or domain reputation. - Unsubscribe Rate
The percentage of subscribers opting out for each campaign. Occasional unsubscribes are normal, but an escalating rate signals you may need to adjust content or frequency. - Spam Complaints
If too many subscribers mark your emails as spam, your domain reputation can plummet, causing deliverability problems. Monitor these complaints and take steps to resolve potential issues. - Return on Investment (ROI)
Tracking how much revenue your campaigns generate, relative to what you spend, is the definitive measure of effectiveness. Many email platforms allow you to connect eCommerce data or track other monetary conversions directly.
Tools and Resources to Simplify Email Marketing
Several tools can supplement your efforts, making campaigns easier to design, test, and track:
- Email Design Tools
Resources like Canva and Adobe Spark help you design consistent, eye-catching banners or small graphics for your emails. Custom imagery can distinguish your brand in crowded inboxes. - Email Rendering and Testing
Tools like Litmus or Email on Acid preview how your messages appear in various email clients (Gmail, Outlook, Apple Mail, etc.) and on different devices. Spotting layout or formatting issues before sending can prevent embarrassing mistakes. - CRM Integration
Connecting your Customer Relationship Management system with your email platform (or choosing one that includes CRM) offers a single source of truth for all customer data. This integration makes segmentation and personalization more accurate. - Analytics and Tracking
While most email platforms provide basic analytics, adding Google Analytics UTM parameters to links can provide deeper insights. Track subscriber behavior on your website after they click through an email. - Project Management Tools
Tools like Trello, Asana, or Monday.com can keep track of your email production schedule, ensuring each campaign is planned, designed, tested, and sent on time.
Creating a Sustainable Email Marketing Strategy
Email marketing shouldn’t be approached as a one-off tactic. Building a sustainable strategy involves:
- Regular Scheduling
Whether it’s a weekly newsletter or a monthly product roundup, consistency helps subscribers know what to expect. Keep a schedule that is manageable and doesn’t compromise quality. - Content Variety
Within your chosen schedule, mix up content types. One email could be a deep-dive article, another a curated list of industry news, and another a promotional offer. Varying content keeps your audience engaged. - Customer Lifecycle Integration
Map emails to every stage of the customer journey. Welcome campaigns for new subscribers, educational sequences for leads, promotional emails for prospective buyers, and loyalty-driven messages for repeat purchasers. - Surveys and Feedback
Periodically asking subscribers for their input can guide your content roadmap. You’ll learn what they find most helpful and can align your messaging with their interests. - Goal Reassessment
Business goals evolve. As your organization grows, revisit your email marketing objectives. Are you now aiming for brand awareness over direct sales? Adjust your tactics, content, and segmentation accordingly.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Observing how others succeed can inspire new strategies:
- Small Retailer With Limited Budget
A small clothing boutique launched a monthly newsletter highlighting new arrivals, styling tips, and local events. Despite having only a few hundred subscribers, the boutique consistently promoted in-store events and used a compelling lead magnet—an exclusive fashion guide—for new sign-ups. Over a year, the open rate hovered above 40%, and the boutique reported a 15% growth in revenue attributed to email campaigns. - Tech Startup Automating Onboarding
A SaaS (Software as a Service) startup created a six-part onboarding sequence for new users. Each email contained a short instructional video demonstrating a core feature. After implementing this sequence, the startup saw a 20% increase in user retention and a 25% decrease in the number of support tickets, as new users understood how to leverage the product quickly. - eCommerce Store Using Abandoned Cart Emails
An online furniture store introduced a three-part abandoned cart series. The first email reminded users of their cart 24 hours after abandonment. The second email arrived 48 hours later with a 10% discount offer. The final email, after 72 hours, provided testimonials and free shipping. The store recovered nearly 30% of the carts that were initially abandoned.
Overcoming Challenges
All marketers encounter hurdles at some point:
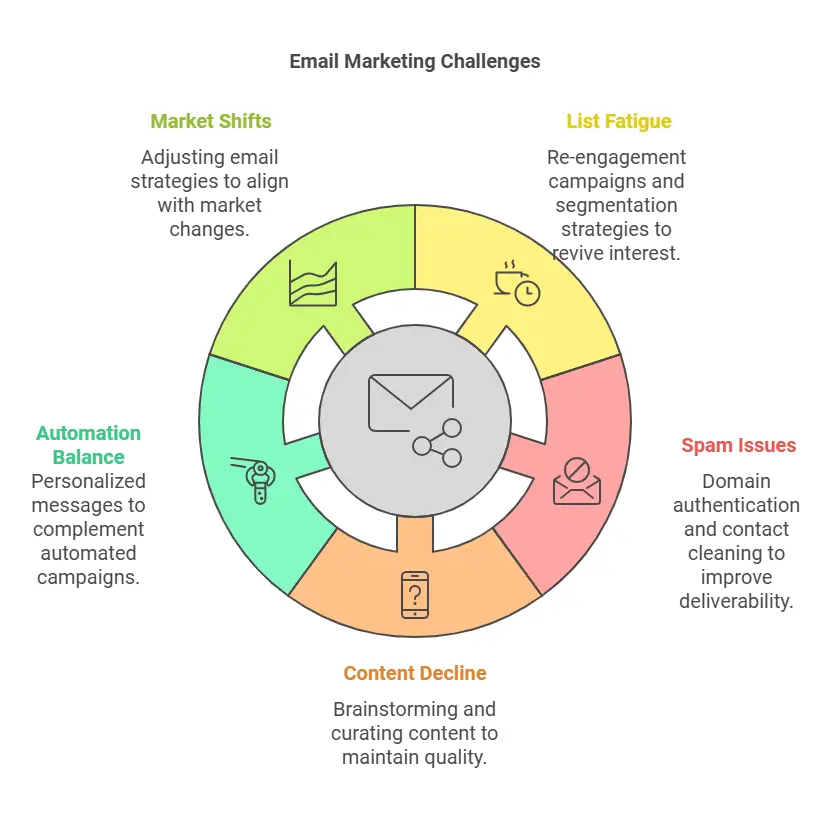
- List Fatigue
If open rates and click-through rates drop over time, or unsubscribe rates rise, consider launching a re-engagement campaign with fresh content or limited-time offers. Segment out the most disengaged subscribers for a last-chance campaign before removing them to improve deliverability. - Spam and Deliverability Issues
If emails start landing in spam folders, investigate whether you have an issue with your sender domain’s reputation. Steps can include authenticating your domain with DKIM and SPF, cleaning out stale contacts, and adjusting your frequency. - Content Quality Decline
Maintaining fresh, high-quality content requires research and creativity. If you hit a slump, brainstorm new angles, curate relevant industry news, or ask subscribers for questions that you can address in your emails. - Balancing Automation and Human Touch
Automation is powerful, but it can feel impersonal if overused. Balance automated campaigns with occasional personalized notes. For example, if a high-value customer hits a milestone, send them a personalized celebratory message. - Shifting Market Conditions
External factors—like changes in consumer sentiment or economic downturns—can influence email performance. Keep an eye on open rates and engagement in context with broader market shifts. If necessary, adjust messaging, tone, or frequency to remain relevant and sensitive.
Scaling Your Email Marketing Efforts
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can expand your efforts:
- Advanced Personalization
If you’ve integrated with a robust CRM, you can leverage data such as browsing history, past purchases, or location details to make more targeted recommendations. - Dynamic Content
Some email platforms allow dynamic sections that change content based on subscriber attributes. This allows you to send one email, but show different product recommendations or messaging for each segment. - Lead Scoring
Businesses with complex sales cycles can implement lead scoring to identify which subscribers show the most potential. High-scoring leads might receive more frequent or personalized communications. - Multi-Channel Nurturing
Email can work alongside other channels. A user who clicks an email offer could receive retargeting ads on social media, reinforcing the same message and funneling them toward conversion. - Expansion into Specialized Automation
From reactivation campaigns for long-lost customers to loyalty program updates, there’s always room to add new automated sequences. Each new funnel can nurture a different subset of subscribers based on interactions or lifecycle stages.
Email Marketing Compliance and Regulations
Regulatory frameworks such as GDPR in Europe and CAN-SPAM in the United States exist to protect consumer privacy and combat spam. Observing these laws isn’t just about avoiding legal trouble; it also enhances subscriber trust:
- Obtain Explicit Consent
Never add someone to your email list without their permission. Avoid pre-checked boxes on sign-up forms. Always let people choose to opt in. - Provide Unsubscribe Options
Every marketing email must include a clear and functional “unsubscribe” link. Make sure the opt-out process is straightforward and honored promptly. - Include Your Physical Address
Most regulations require including your valid physical mailing address in the email footer. This further establishes authenticity. - Be Transparent
Disclose how you will use subscriber data. Link to your privacy policy if you collect personal information beyond just email addresses. - Honor Data Access Requests
Under regulations like GDPR, individuals have the right to access the data you store about them. Be prepared to fulfill such requests or delete their data if they ask.
Maintaining a Healthy Sender Reputation
Sender reputation is a score that ISPs use to decide whether your emails land in inboxes or get flagged as spam. Strategies to keep your reputation robust include:
- Use Double Opt-In
When someone signs up, send a confirmation email that requires them to click a link to verify their subscription. This confirms their interest and ensures your list stays clean. - Monitor Bounce Rates
High bounce rates arise from invalid or old email addresses. Routinely remove bounced addresses to show ISPs you’re a responsible sender. - Low Spam Complaints
Consistently sending relevant content to an interested audience will keep complaints down. If complaints spike, reevaluate your content, frequency, and segmentation strategies. - Authentication Protocols
Set up DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) and SPF (Sender Policy Framework) to verify your identity with email servers. DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) can add another layer of protection against spoofing. - Gradual Scaling
If you recently started with a new domain or IP address, ramp up your sending volume gradually. Sudden spikes can trigger red flags, as spammers often appear with large volumes of emails suddenly.
Future Trends in Email Marketing
Technology and consumer behavior evolve, influencing how email marketing is executed:
- Interactive Emails
Movable elements like sliders, collapsible menus, or embedded quizzes can reduce friction by allowing recipients to interact directly with the email. Such emails can increase engagement but may require advanced HTML and CSS skills. - AI-Driven Personalization
Algorithms can predict which products or topics a subscriber is most likely to engage with, tailoring email content at scale. This goes beyond basic personalization and can significantly improve conversion rates. - AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) for Email
AMP for email enables more dynamic experiences, such as RSVPing to events or filling out forms without leaving the inbox. As more providers support AMP, users can accomplish tasks directly within an email. - More Sophisticated Automation
Integration with social media and other platforms can trigger personalized sequences for complex user journeys. Scoring models that track multiple data points in real time will guide hyper-specific email content. - Privacy-Focused Marketing
Changes in privacy regulations and user preferences may reduce the data available to marketers. Building transparent, respectful, and trust-based relationships will be more vital than ever.
Putting It All Together
A sustainable and effective email marketing program weaves together quality content, strategic segmentation, thoughtful automation, and vigilant monitoring of performance and deliverability. Here’s a quick step-by-step recap of the process:
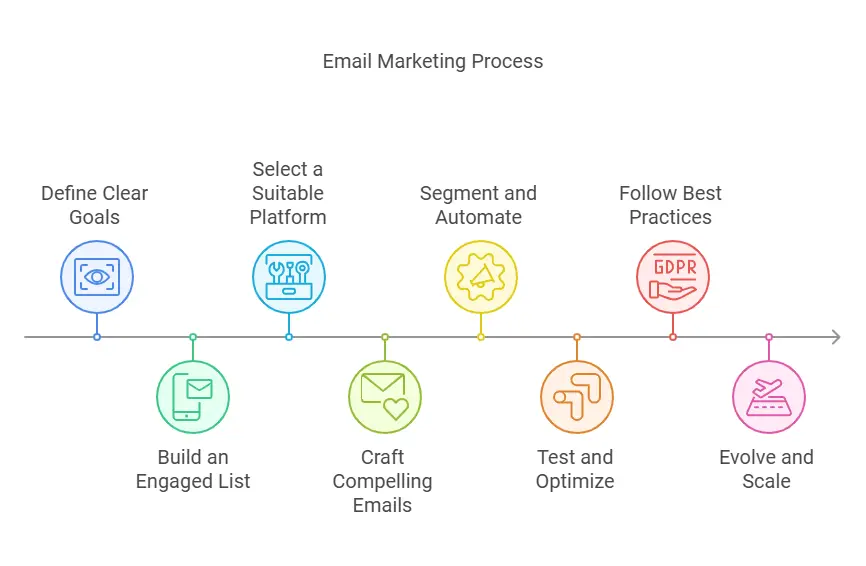
- Define Clear Goals
Know what you hope to achieve, whether it’s brand awareness, lead nurturing, or driving immediate sales. - Build an Engaged List
Use strategic sign-up forms, compelling lead magnets, and social promotions to grow your list organically with interested subscribers. - Select a Suitable Platform
Choose a tool that aligns with your needs, whether it’s simplicity, advanced automation, or robust analytics. - Craft Compelling Emails
Design with mobile in mind, use concise subject lines, engaging content, relevant visuals, and a single clear CTA. - Segment and Automate
Divide subscribers by demographics, behaviors, or stages in the customer journey. Automate welcome sequences, drip campaigns, and abandoned cart reminders. - Test and Optimize
Conduct A/B tests on subject lines, content, and send times. Refine your approach based on metrics like open rates, click-through rates, and conversions. - Follow Best Practices
Respect subscriber preferences, stay compliant with relevant laws, and maintain a strong sender reputation. - Evolve and Scale
As your business grows, explore advanced personalization, interactive email features, and more sophisticated segmentation to maintain relevance and engagement.
Conclusion
Email marketing remains a cornerstone of a robust digital marketing strategy. The direct access to subscribers’ inboxes, combined with the channel’s outstanding ROI, makes it a crucial part of any campaign intended to drive traffic, sales, or brand awareness. Through a focus on list-building, thoughtful campaign planning, effective design, and strategic automation, you can deliver messages that resonate with your audience at every stage of their journey.
A data-driven, iterative approach lets you refine subject lines, content, and timing to optimize results over time. By nurturing your contacts and respecting their preferences, you’ll see higher engagement and fewer unsubscribes. Consistency in design and voice will solidify your brand identity across all communications, while regular testing ensures your efforts remain relevant in a competitive market.
Email marketing is both an art and a science—combining creativity in content development and design with the technical know-how of segmentation, compliance, and deliverability. When executed well, it can become a reliable source of revenue, brand loyalty, and thought leadership in your niche. Even as new platforms and technologies emerge, email stands firm as a channel that practically every user has and engages with.
Take the initiative to launch or refine your email marketing efforts now. Align your objectives, choose a suitable platform, craft compelling messages, and keep testing. Over time, you’ll see the compounding returns of a well-tuned email strategy in higher sales, strong relationships with your subscribers, and a recognizable presence in inboxes everywhere.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is email marketing still relevant today?
Email marketing enables direct, personalized communication with audiences. With high inbox engagement, it remains cost-effective for promotions, content sharing, and customer retention, driving high ROI compared to other digital channels.
What are the key components of a strong email strategy?
A strong email strategy includes a quality subscriber list, segmentation for targeted messaging, engaging content, and tracking key metrics. These elements enhance open rates, customer engagement, and conversions, ensuring better performance and marketing success.
How can businesses grow their email subscriber list?
Businesses can grow email lists by using sign-up forms, offering lead magnets like eBooks or discounts, and leveraging social media. Clear value propositions and user-friendly sign-ups boost opt-ins, ensuring a steady flow of engaged subscribers.
Why is personalization important in email marketing?
Personalization tailors emails to a subscriber’s preferences, behaviors, and demographics. This increases engagement, boosts open and click-through rates, and fosters customer loyalty, making campaigns more effective and conversion-driven.
How do businesses measure email marketing success?
Businesses track email success through open rates, click-through rates, and conversions. Unsubscribe rates and engagement levels also indicate effectiveness. Analyzing these metrics helps refine future campaigns for better audience targeting and improved ROI.
Further reading
Campaign Monitor. “Getting Started with Email Marketing.” Campaign Monitor. Accessed March 7, 2025. https://www.campaignmonitor.com/resources/guides/getting-started-with-email-marketing/.
HubSpot. “Email Marketing Software & Tools.” HubSpot. Accessed March 7, 2025. https://www.hubspot.com/products/marketing/email.
Mailchimp. “Email Marketing Benchmarks.” Mailchimp Resources. Accessed March 7, 2025. https://mailchimp.com/resources/email-marketing-benchmarks/.
Squarespace. “Email Marketing.” Squarespace. Accessed March 7, 2025. https://www.squarespace.com/email-marketing.
Zapier. “Best Free Email Marketing Software for 2024.” Zapier Blog. Accessed March 7, 2025. https://zapier.com/blog/free-email-marketing-software/.
Neil Patel. “Email Marketing for Beginners: How to Get Started.” YouTube Video, 15:34. February 15, 2023. Accessed March 7, 2025. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xnbr9ARrKrg.
HubSpot Marketing. “How to Send Better Marketing Emails.” YouTube Video, 8:52. January 5, 2023. Accessed March 7, 2025. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qB1X0UavKIs.







