Introduction to Business Strategy
A business strategy is the backbone of any successful organization, serving as the foundation for structured growth and competitive advantage. It provides a clear roadmap for achieving organizational goals, ensuring that all resources—whether financial, human, or technological—are aligned toward shared objectives. By defining priorities and setting measurable targets, a well-thought-out strategy enables businesses to make informed decisions and respond effectively to changing market dynamics. It helps identify opportunities, mitigate risks, and optimize operations, making it indispensable for navigating today’s complex and competitive environment.
Whether you are a startup entrepreneur striving to carve out your niche or a seasoned executive steering a large enterprise, understanding and crafting a robust business strategy is a critical skill. It not only drives immediate results but also lays the groundwork for sustained long-term success. In this article, we’ll delve into the core components of a strong business strategy, examine its significance in achieving organizational excellence, and provide actionable steps to develop and implement one effectively, ensuring sustainable growth and resilience in an ever-evolving marketplace.
What is Business Strategy?
Business strategy refers to a set of decisions and actions designed to achieve business goals and secure a competitive edge in the market. It encompasses how a company plans to use its resources, processes, and relationships to deliver value to customers and stakeholders.
A strong business strategy defines the organization’s vision, sets measurable objectives, and establishes a clear path for execution. It also ensures that resources are allocated efficiently and that the company can adapt to changing market conditions. By aligning operations with strategic priorities, a well-crafted business strategy enables organizations to anticipate challenges, seize opportunities, and drive long-term growth and profitability.
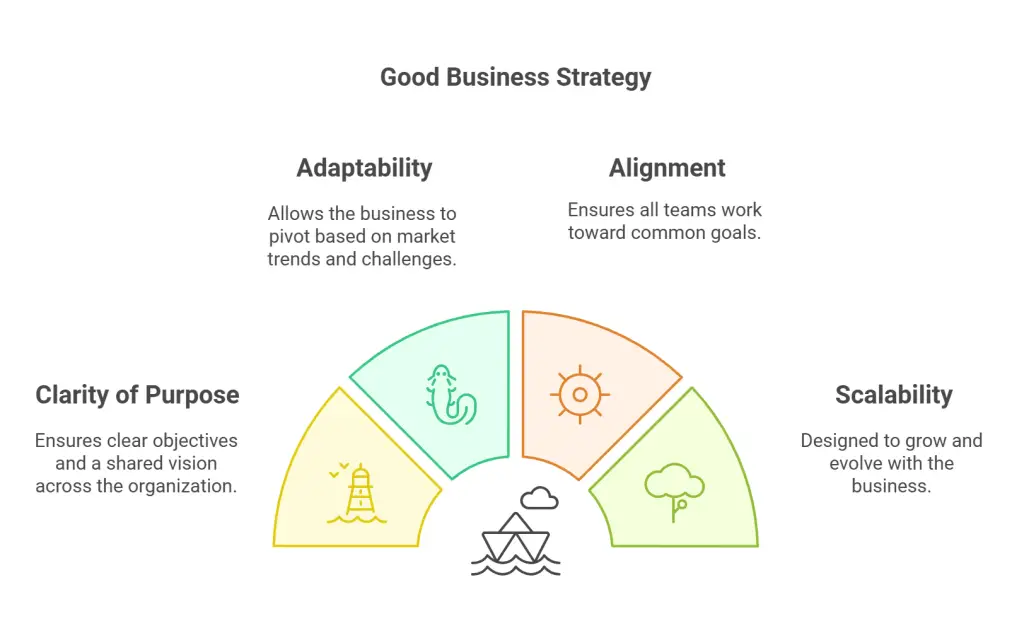
Key Characteristics of a Good Business Strategy:
- Clarity of Purpose: Clear objectives and a shared vision across the organization.
- Adaptability: The ability to pivot based on market trends and unforeseen challenges.
- Alignment: Ensuring all departments and teams are working toward common goals.
- Scalability: Designed to grow and evolve as the business expands.
Why is a Business Strategy Important?
A business strategy is crucial because it provides a clear roadmap for achieving organizational goals, ensuring all efforts are aligned with a common vision. It helps businesses define their unique value proposition, navigate competitive markets, and adapt to changing conditions.
A well-crafted strategy enables efficient resource allocation, prioritizes initiatives with the highest impact, and fosters consistent decision-making across teams. Additionally, it provides measurable benchmarks to track progress, identify challenges, and make necessary adjustments. By offering direction, focus, and a framework for growth, a strong business strategy is essential for long-term success and sustainability.
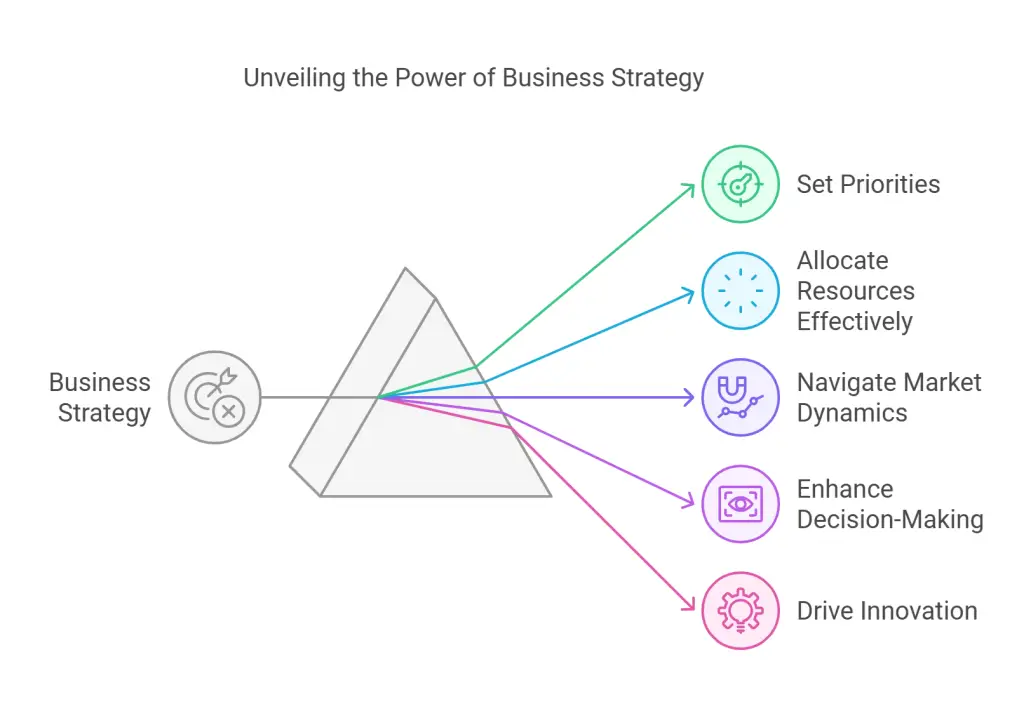
A business strategy serves as a guiding framework, enabling organizations to:
- Set Priorities: Identify the most critical initiatives that align with the company’s goals.
- Allocate Resources Effectively: Optimize financial, human, and technological assets.
- Navigate Market Dynamics: Stay competitive in a rapidly changing business environment.
- Enhance Decision-Making: Provide clarity and focus for leaders and teams.
- Drive Innovation: Foster a culture of innovation by defining clear areas of focus.
Components of an Effective Business Strategy
1. Vision and Mission Statements
A compelling vision and mission form the foundation of any strategy, articulating the company’s aspirations and the purpose it serves. The vision sets a long-term direction, inspiring both employees and stakeholders by painting a clear picture of the desired future.
The mission, on the other hand, defines the organization’s core purpose and how it intends to achieve its goals, guiding everyday decisions and actions. Together, these elements provide a framework that aligns strategic initiatives with the organization’s broader objectives, ensuring consistency and focus at every level.
Regularly revisiting and communicating the vision and mission fosters a sense of unity and shared purpose, driving the organization toward sustained success.
For example:
- Vision: “To be the most customer-centric company in the world.”
- Mission: “To deliver innovative solutions that simplify daily life.”
2. Core Values
Core values establish the foundational principles that guide an organization’s behavior and decision-making. They shape the company culture, providing a sense of purpose and direction for employees while influencing how the organization interacts with stakeholders. Clearly defined values foster consistency and integrity in actions, aligning day-to-day operations with the company’s broader mission.
Beyond shaping culture, core values also serve as a benchmark for evaluating strategic initiatives. Decisions and strategies are more effective when they align with the organization’s principles, ensuring long-term coherence and trust with customers, employees, and partners. Regularly revisiting and reinforcing these values helps maintain relevance and unity as the organization grows and evolves.
3. Market Analysis
Understanding the external environment is critical. Conduct a thorough analysis of industry trends, customer needs, and competitor activities using tools like SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) and PESTLE (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental).
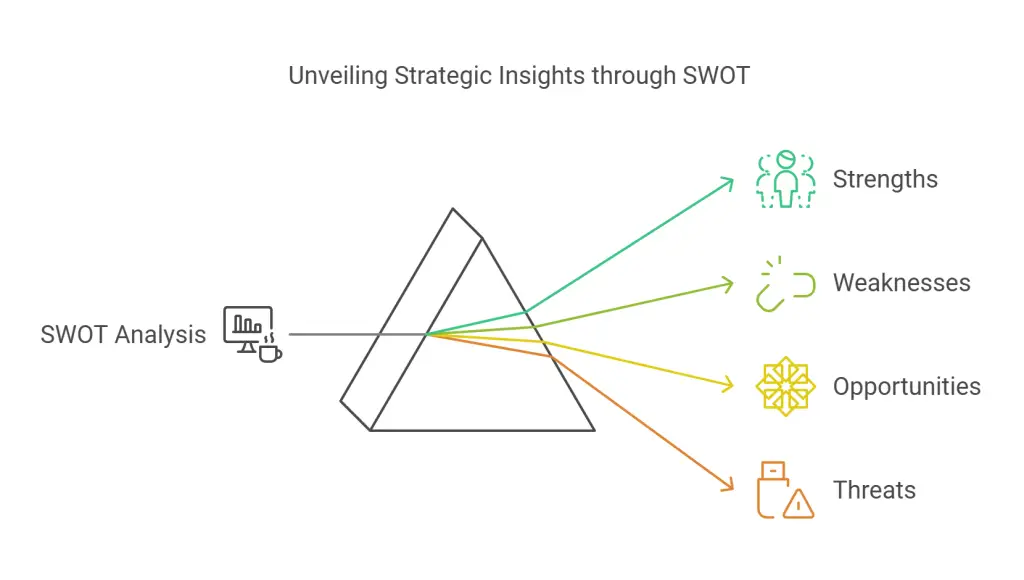
SWOT Analysis in Practice
A thorough SWOT analysis is not just about listing factors but also about assessing their impact on strategic decisions. For example:
- Strengths: Highlight capabilities like proprietary technology, a skilled workforce, or an established brand.
- Weaknesses: Address areas such as outdated processes, limited financial resources, or dependency on a single supplier.
- Opportunities: Pinpoint trends like emerging markets, technological advancements, or demographic shifts.
- Threats: Identify risks such as new competitors, regulatory changes, or economic downturns.
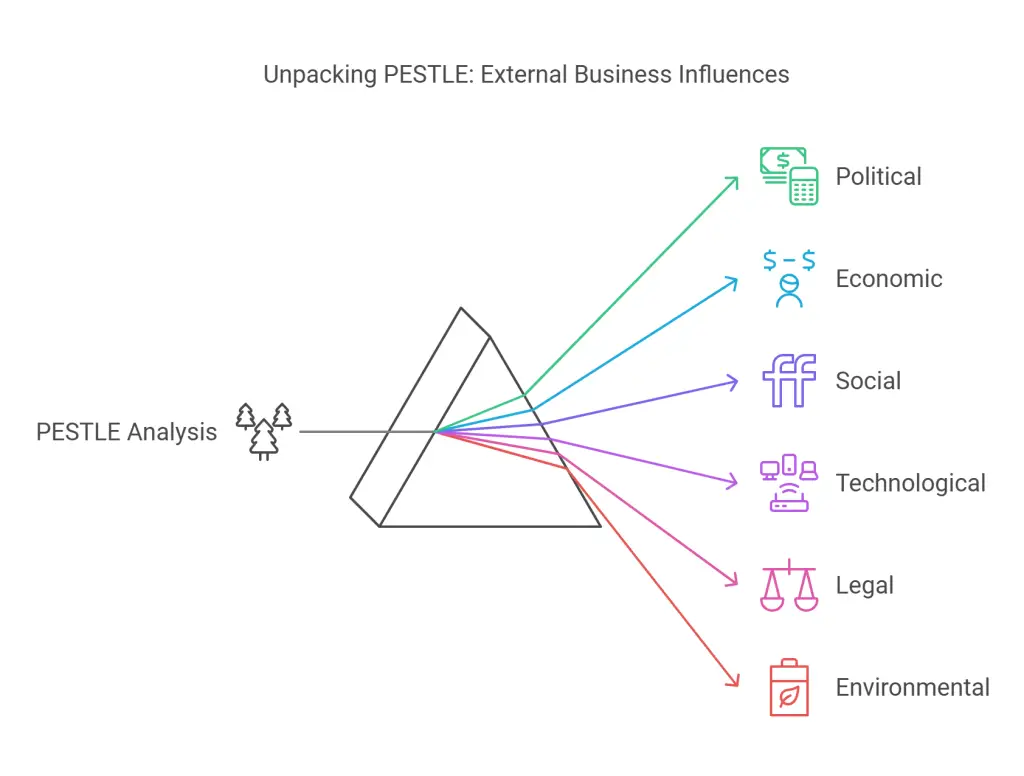
PESTLE Analysis
A PESTLE analysis dives deeper into external factors influencing your business. For instance:
- Political: Assess government policies, trade tariffs, and political stability.
- Economic: Examine inflation rates, consumer spending habits, and economic cycles.
- Social: Understand demographic changes, cultural trends, and consumer behavior shifts.
- Technological: Track emerging technologies, automation, and R&D advancements.
- Legal: Consider regulatory compliance, labor laws, and intellectual property issues.
- Environmental: Evaluate sustainability demands and environmental regulations.
4. Goals and Objectives
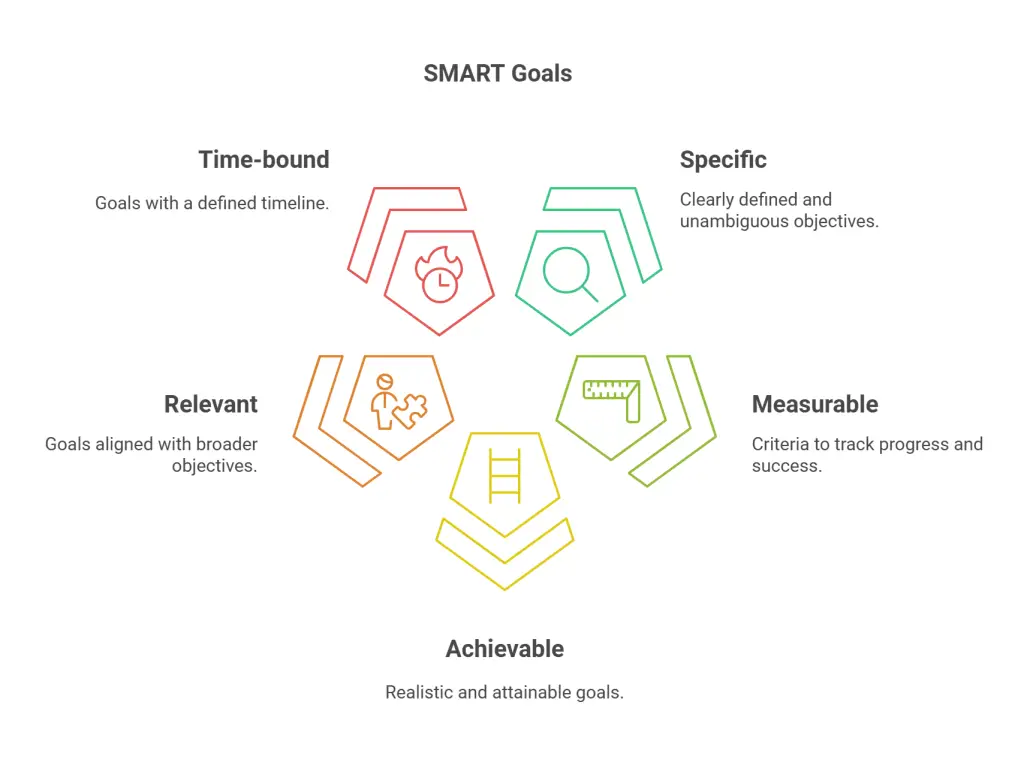
Set SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals. For instance:
- Increase market share by 10% in the next 12 months.
- Launch two new products within the fiscal year.
Breaking down goals into short-term, medium-term, and long-term objectives can also provide clarity and direction. Short-term goals may focus on operational improvements, while long-term goals align with visionary aspirations.
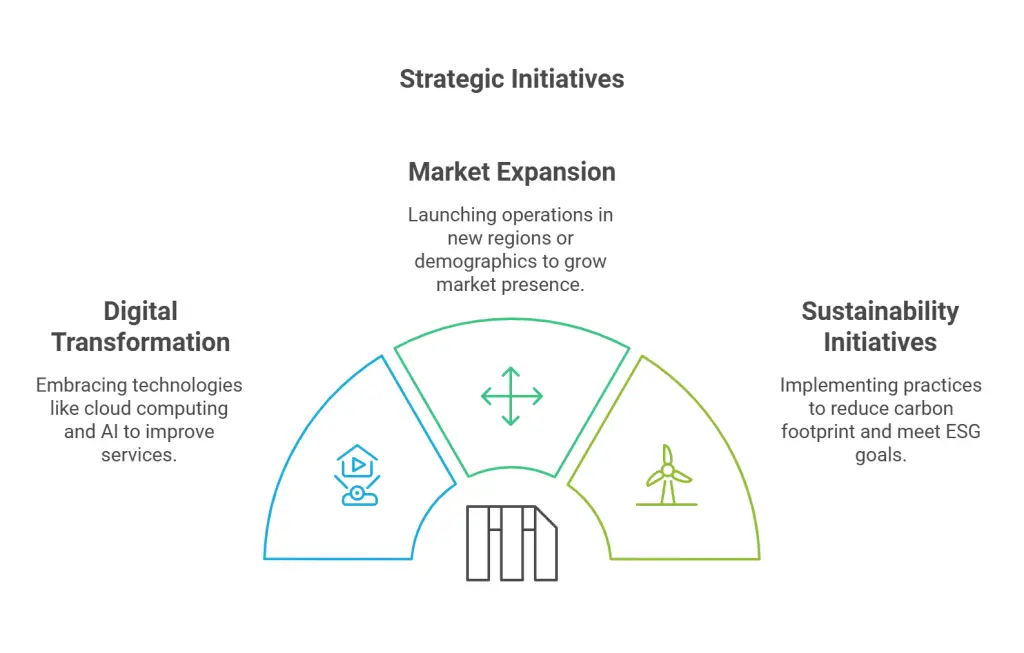
5. Strategic Initiatives
Define key initiatives that will help achieve your objectives. These could include entering new markets, adopting new technologies, or forming strategic partnerships. Examples include:
- Digital Transformation: Embracing cloud computing or AI to enhance customer service.
- Market Expansion: Launching operations in underserved regions or new demographics.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Reducing the carbon footprint to meet ESG goals.
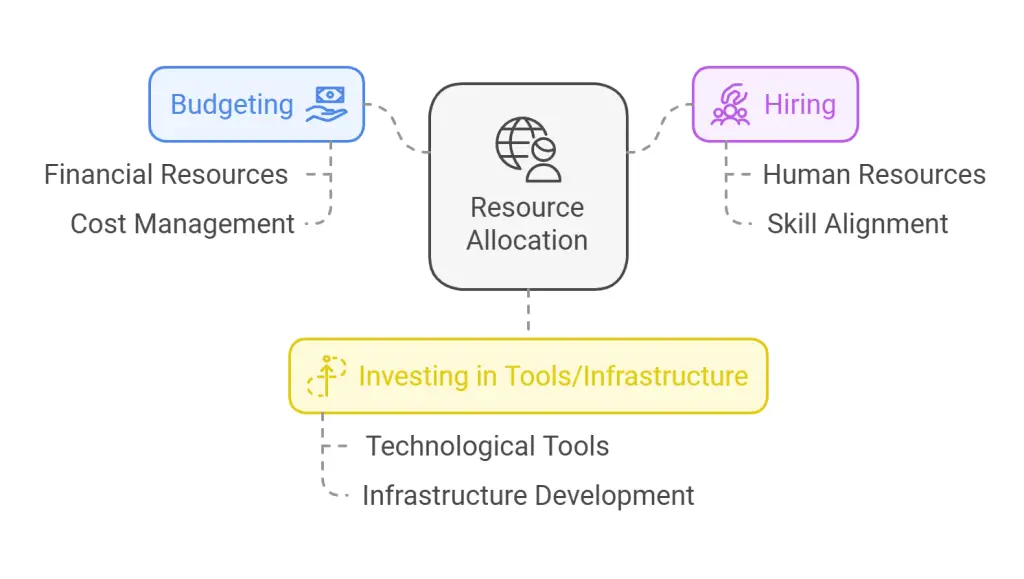
6. Resource Allocation
Develop a resource allocation plan to ensure the effective use of budgets, personnel, and tools required for strategic execution. This involves prioritizing spending, hiring the right talent, and investing in essential infrastructure. Utilizing a resource matrix can help align financial and human resources with key objectives, maximizing efficiency and impact while avoiding resource gaps or overlaps.
In addition to aligning resources, continuously monitor and adjust allocations based on changing needs and performance outcomes. Regular reviews of resource usage can identify inefficiencies or areas where additional investment is required. Building flexibility into the resource plan allows the organization to adapt quickly to unexpected challenges or opportunities, ensuring that critical objectives remain on track without unnecessary delays.
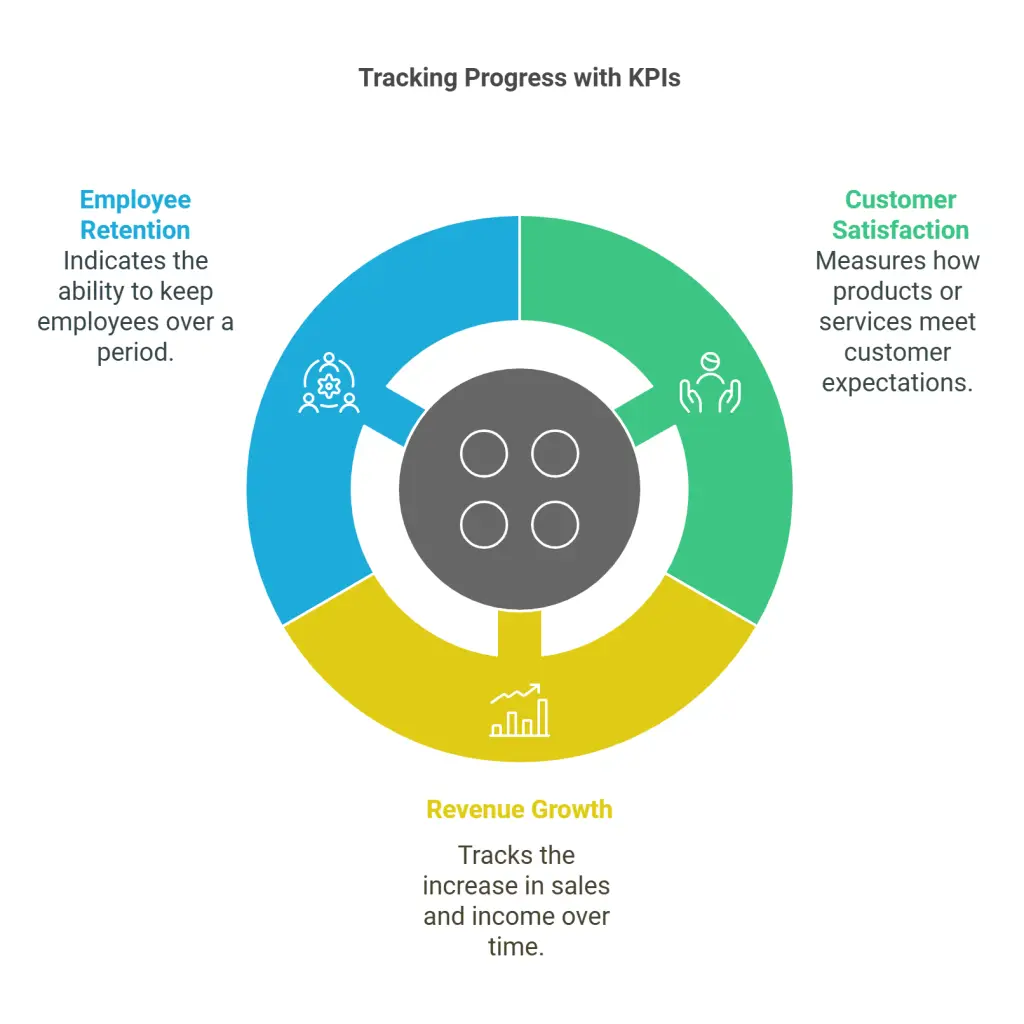
7. KPIs and Metrics
Track progress with Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure success and maintain focus on strategic goals. Use metrics such as customer satisfaction scores, revenue growth rates, and employee retention to gain insights into performance. Regular reviews of these indicators help identify trends, ensure alignment with objectives, and flag potential challenges early, enabling timely course corrections and continuous improvement.
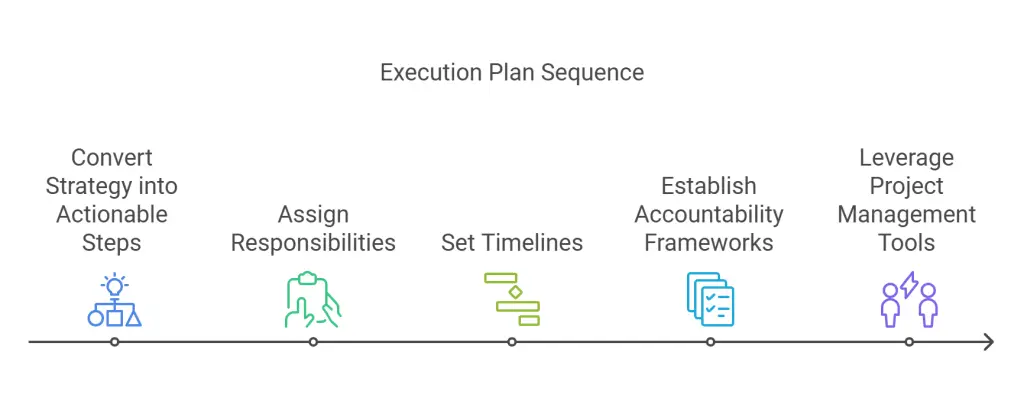
8. Execution Plan
Convert your strategy into clear, actionable steps by breaking it into smaller, manageable tasks. Assign responsibilities to individuals or teams, ensuring everyone understands their role and deadlines. Establish accountability systems, such as regular progress updates or performance reviews, to track execution and address any issues promptly.
In addition to defining tasks, create an environment where collaboration and communication thrive. Using tools like Asana, Trello, or similar platforms can centralize task management and improve efficiency. Regularly reviewing milestones and adapting the plan as needed ensures alignment with overall goals and timely adjustments to unforeseen challenges. A robust execution framework transforms strategy into tangible results.
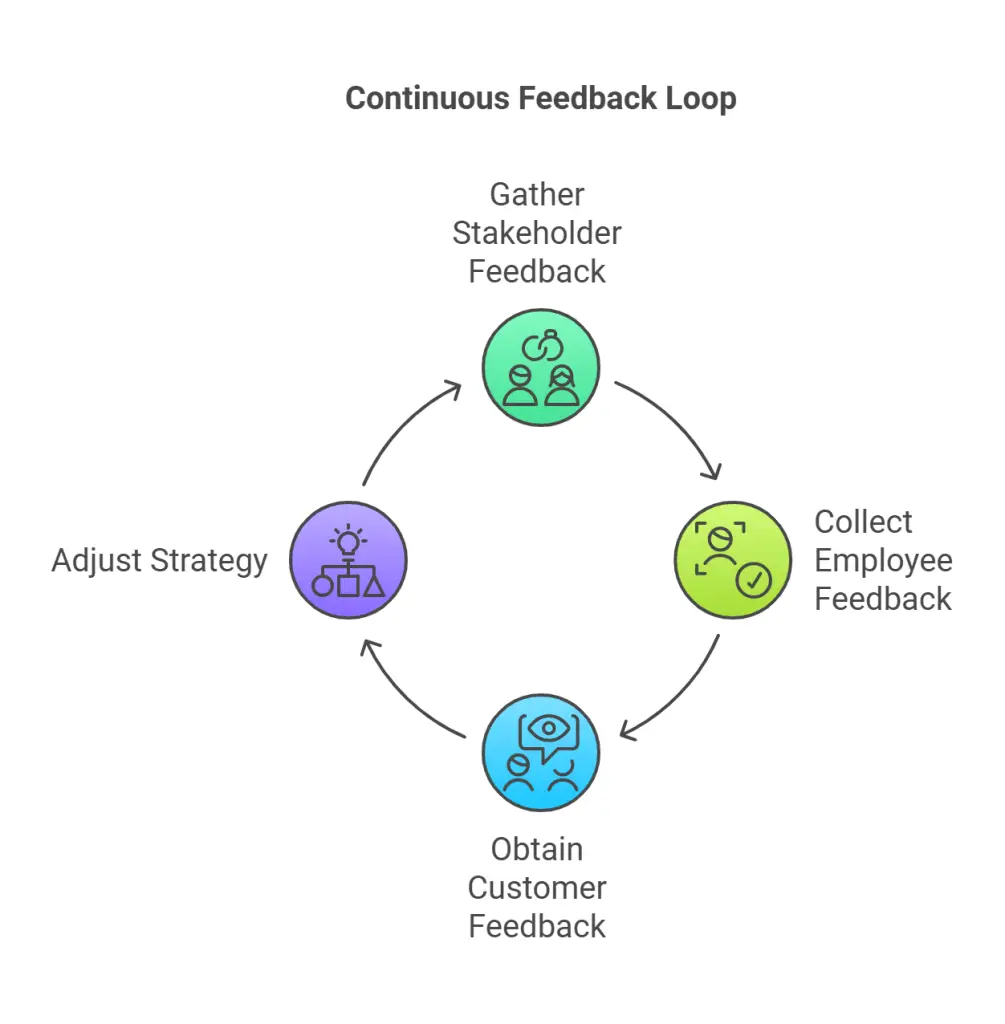
9. Feedback Loops
Create structured mechanisms for collecting, analyzing, and acting on feedback from a diverse range of stakeholders, including employees, customers, partners, and other relevant parties. These mechanisms could include regular surveys, focus groups, performance reviews, and open forums for suggestions.
Such an approach not only ensures that the strategy remains aligned with evolving market conditions and stakeholder expectations but also fosters a culture of inclusivity and continuous improvement. By actively listening to feedback and incorporating insights into the strategic process, businesses can proactively address challenges, seize opportunities, and refine their objectives.
Additionally, leveraging technology like analytics tools and customer relationship management (CRM) systems can enhance the collection and processing of feedback, providing data-driven insights for informed decision-making. Establishing clear communication channels and setting consistent schedules for reviews ensures that the feedback loop remains active, driving innovation and ensuring the strategy’s relevance and effectiveness over time.
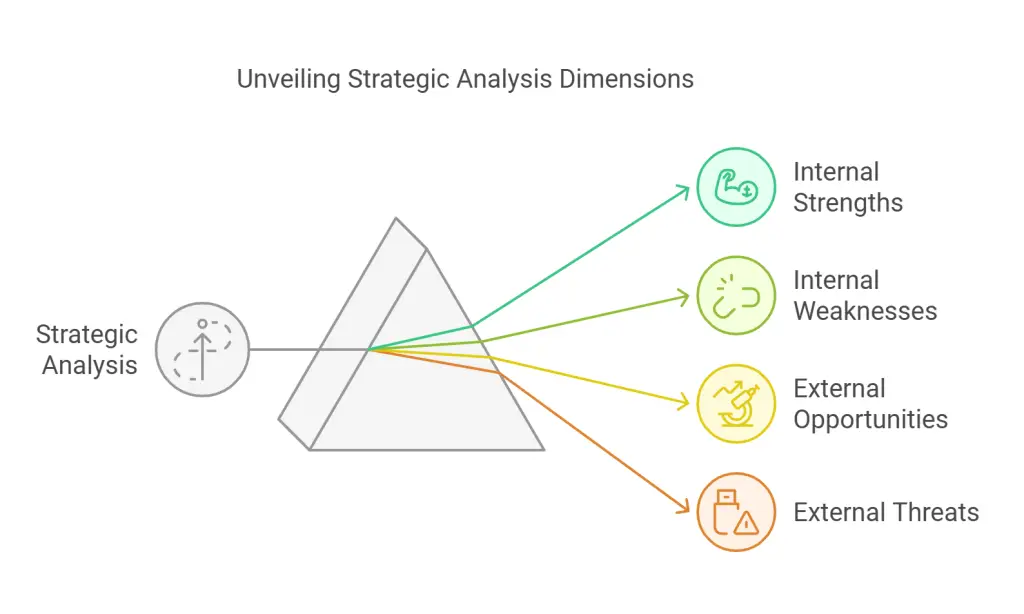
Steps to Develop a Winning Business Strategy
Step 1: Conduct a Strategic Analysis
Begin by evaluating every aspect of your organization’s current situation. Examine internal strengths, such as specialized skills or proven processes, and also pinpoint any weaknesses that may be holding back growth or efficiency. Outside the organization, investigate market trends, emerging technologies, and other opportunities that could drive expansion. Keep an eye out for looming threats like competitor innovations, changing regulations, or shifting customer preferences. Use frameworks like SWOT to categorize these findings systematically, and consider competitor benchmarking to understand how your business compares on pricing, quality, and other relevant metrics.
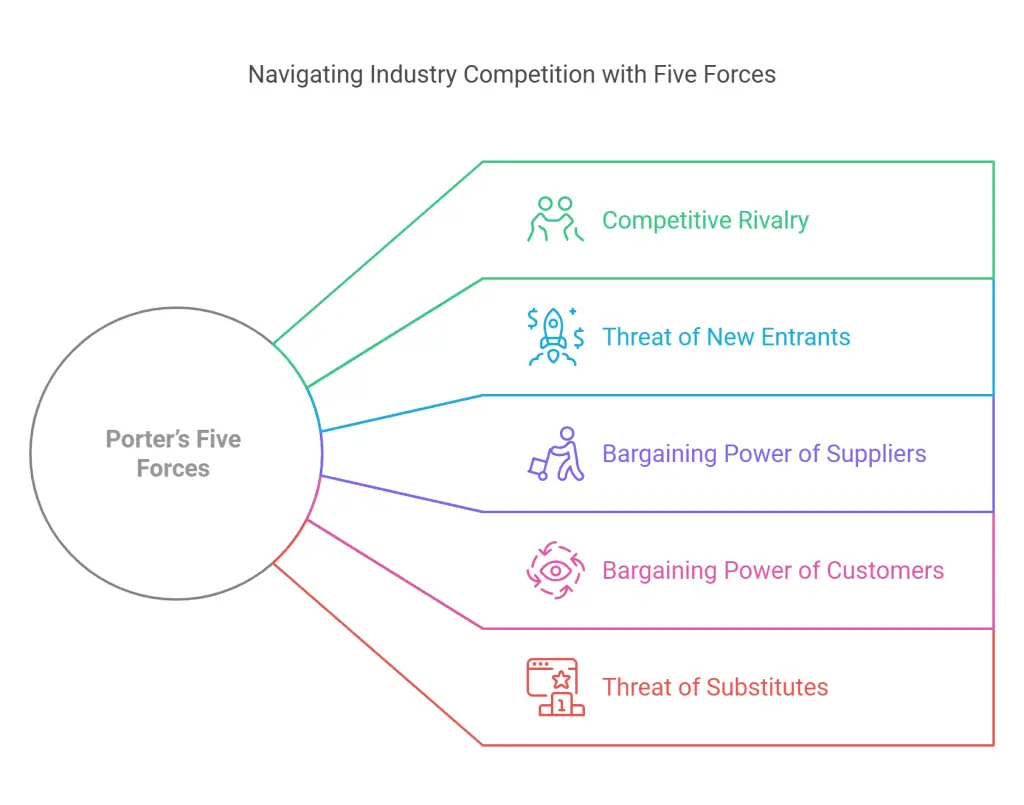
Applying Porter’s Five Forces
Porter’s Five Forces offers a more detailed look at competition within your industry. Begin by analyzing Competitive Rivalry to understand how crowded the market is and whether price wars or aggressive marketing campaigns are common. Next, assess the Threat of New Entrants, focusing on how easily newcomers might disrupt your market share through novel products or aggressive strategies.
Consider the Bargaining Power of Suppliers, ensuring you have multiple sourcing options to reduce cost risks. Similarly, examine the Bargaining Power of Customers—if customers can easily demand lower prices or jump to competitors, you’ll need strategies to maintain loyalty. Lastly, address the Threat of Substitutes, which covers products or services that fulfill the same need differently. By mitigating these forces, your business can carve out a strong position in the market.
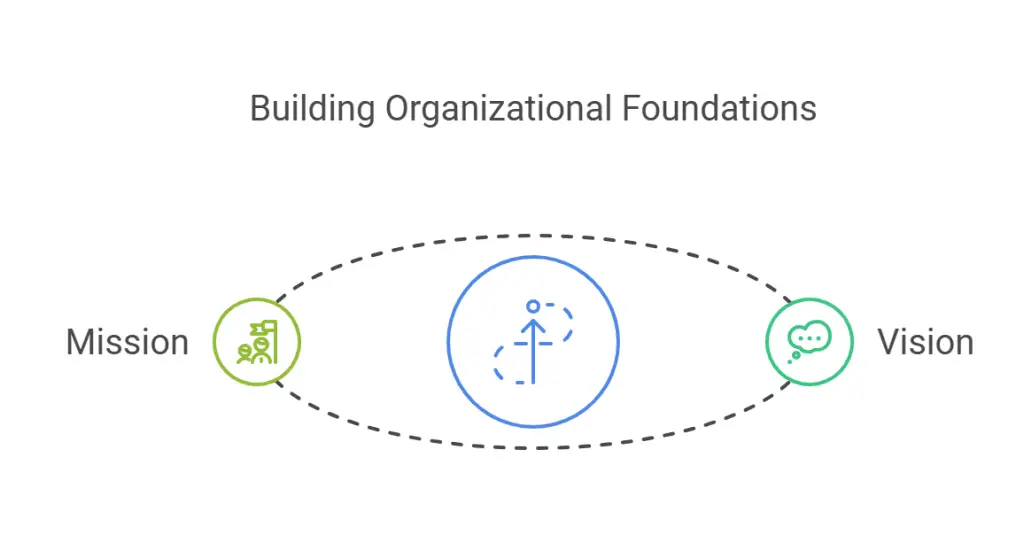
Step 2: Define Your Vision and Mission
Articulate a compelling vision that outlines the ultimate goal for your organization. This vision helps unite everyone around a shared understanding of where you’re headed and what impact you aim to have. Alongside the vision, your mission statement should define your company’s core purpose and values. These foundational elements serve as consistent guides whenever you’re making big decisions about new products, expansions, or strategic shifts.
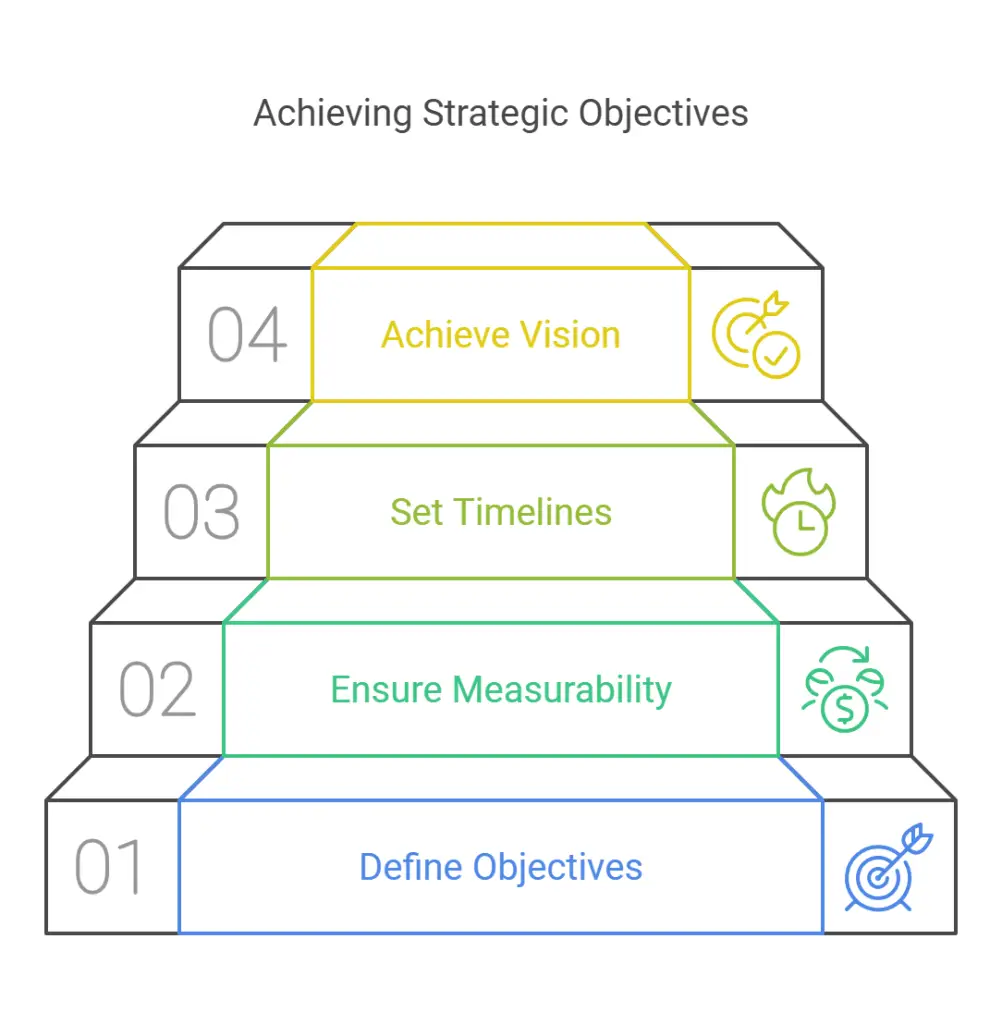
Step 3: Set Clear Objectives
Translate the overarching vision into well-defined objectives that are realistic and achievable. These objectives must be measurable so you can track progress effectively. By adding concrete timelines, you give each objective a sense of urgency, ensuring the organization remains focused on delivering results. For instance, if the vision includes becoming a market leader in customer satisfaction, your objective might be to achieve a specific customer satisfaction score by the end of the year.
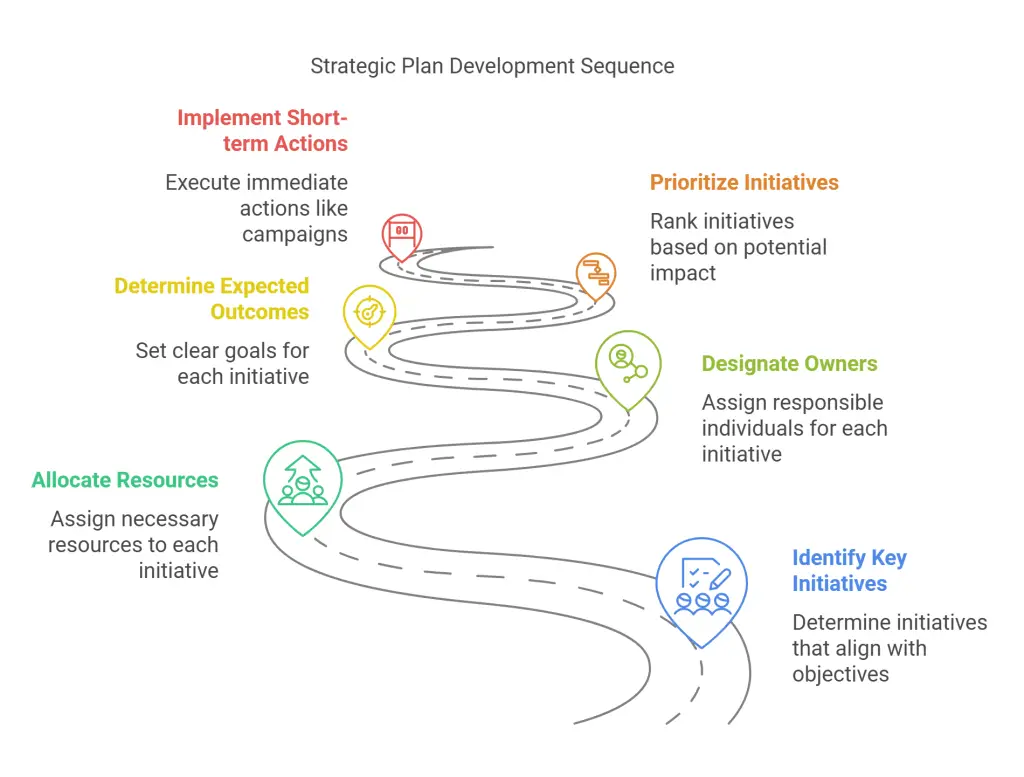
Step 4: Develop a Strategic Plan
Outline the key initiatives that will propel you toward your objectives. Each initiative should have allocated resources, designated owners, and expected outcomes. Prioritize those with the greatest potential for revenue growth, brand development, or operational efficiency. Consider short-term actions—like marketing campaigns or hiring decisions—and long-term moves such as investing in research and development or forming strategic partnerships. An organized, data-driven plan helps keep everyone clear on responsibilities.
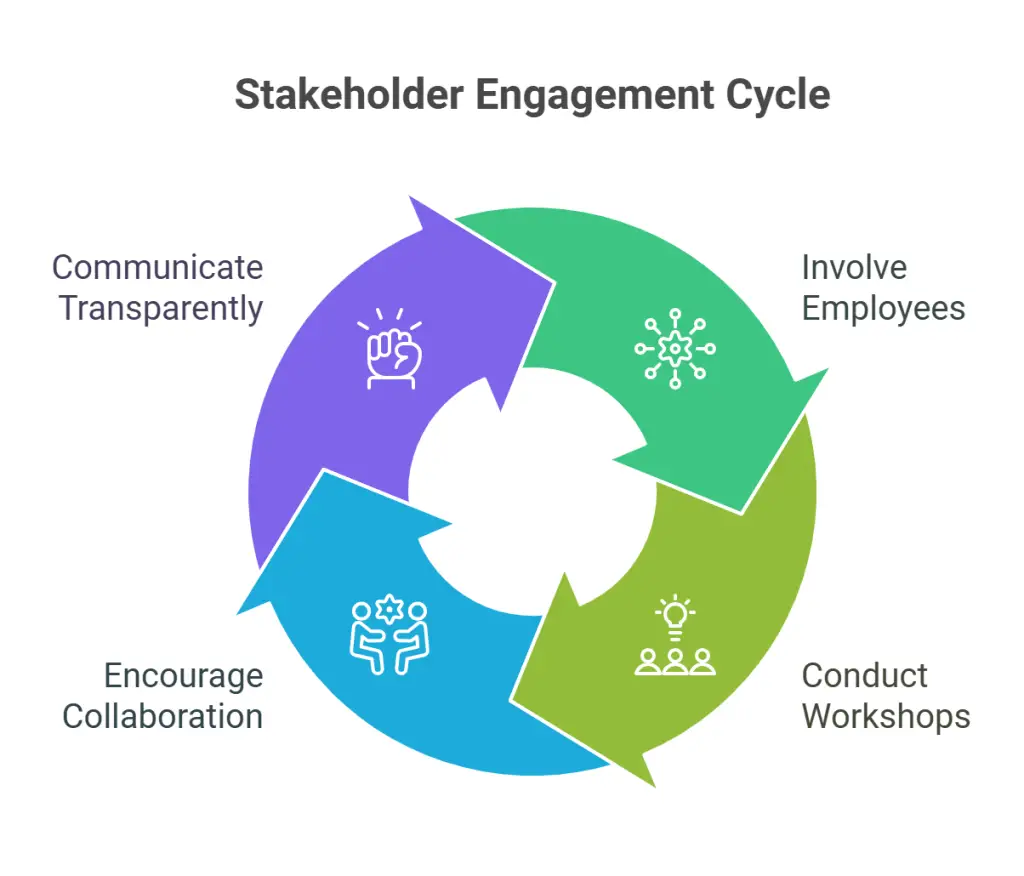
Step 5: Engage Stakeholders
Involve employees at all levels, along with customers and partners, to gather diverse perspectives. Conduct workshops or brainstorming sessions to collect input on potential improvements or new ideas. Encouraging this collaboration promotes wider acceptance and accelerates implementation because everyone feels invested in the direction of the company. Additionally, transparent communication builds trust and motivates people to do their part in fulfilling the strategy.
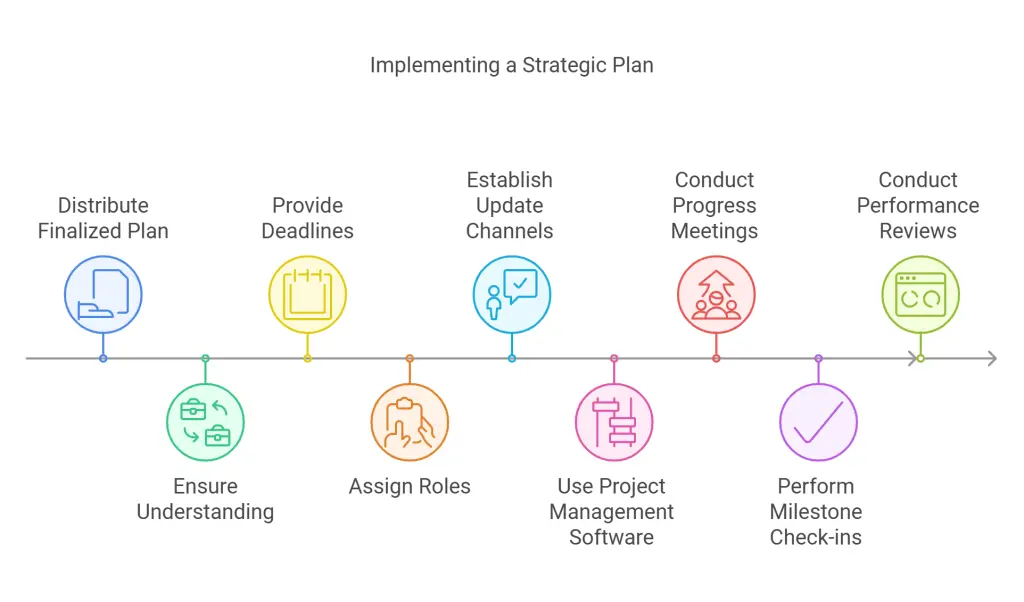
Step 6: Implement the Strategy
Distribute the finalized plan across the organization and ensure each department understands how it aligns with day-to-day operations. Provide clear deadlines, assign roles, and establish the channels for ongoing updates. Project management software can offer task visibility and keep teams aligned on timelines. Regular progress meetings, milestone check-ins, and performance reviews help track accomplishments and highlight any bottlenecks that need attention.
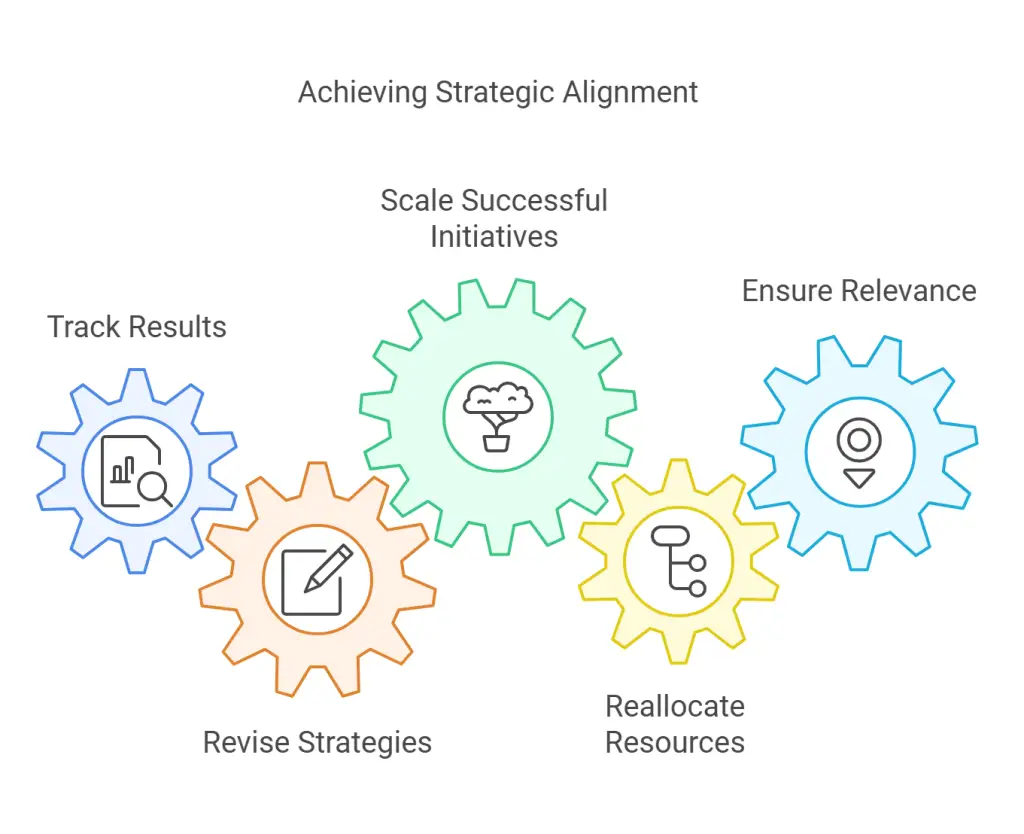
Step 7: Monitor and Adjust
Track results against the specific metrics and objectives you identified early on. If certain strategies aren’t delivering as intended, revise them promptly. This could mean adjusting a marketing campaign, scaling up a successful pilot program, or reallocating resources to more promising initiatives. By staying attentive to market signals, customer feedback, and operational data, you’ll keep the strategy relevant and ensure the business can respond effectively to evolving conditions.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Resistance to Change
Employees may resist new processes or technologies. To overcome this:
- Effective Communication: Clearly articulate the benefits of the strategy. For instance, showcase case studies or examples where similar changes have driven success in comparable organizations.
- Training Programs: Equip teams with the skills to adapt to new tools and practices. Provide hands-on workshops or e-learning modules tailored to specific roles within the organization.
- Leadership Buy-In: Encourage leaders to champion the changes, as their support can motivate teams and reduce skepticism.
Resource Constraints
Limited resources can hinder strategy execution. Solutions include:
- Prioritization: Focus on high-impact initiatives. Create a ranking system to determine which projects align most closely with strategic goals and will yield the highest ROI.
- Partnerships: Collaborate with other organizations to share costs and expertise. For example, small businesses could form consortia to collectively negotiate better supplier rates.
- Incremental Investment: Break down large projects into manageable phases, allowing the company to allocate resources gradually without overextending budgets.
Market Volatility
Economic downturns or rapid industry changes require agility. Strategies include:
- Scenario Planning: Develop contingency plans for different market scenarios. For example, prepare strategies for a 10% decrease in revenue or a sudden supply chain disruption.
- Real-Time Data Analysis: Use analytics to respond quickly to market shifts. Implement tools like dashboards that provide actionable insights into customer trends and operational metrics.
- Flexible Contracts: Negotiate supplier or service agreements that allow for adjustments based on market conditions, such as variable pricing or on-demand scaling.
By addressing these challenges with practical steps, businesses can create a resilient strategy that adapts to both internal and external pressures.
Conclusion
Developing a successful business strategy requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses internal assessments, market analysis, and clear goal-setting. By conducting a thorough strategic analysis, businesses can identify their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, enabling them to make informed decisions.
Defining a clear vision and mission provides direction and purpose, aligning the organization toward common objectives. Setting measurable and time-bound goals translates this vision into actionable steps, facilitating progress tracking and accountability. Engaging stakeholders throughout the process ensures diverse perspectives and fosters buy-in, enhancing the strategy’s effectiveness.
Implementing the strategy with clear communication and resource allocation is crucial for execution, while continuous monitoring and adjustment allow the business to remain agile and responsive to changing conditions. By following these steps, organizations can craft a robust business strategy that drives sustainable growth and secures a competitive edge in the market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the importance of a well-crafted business strategy?
A well-crafted business strategy provides a clear roadmap for growth, helping businesses allocate resources effectively, stay competitive, and adapt to market changes. It ensures alignment across all operations, driving efficiency, profitability, and long-term success.
How can businesses identify their competitive advantage?
Businesses can identify their competitive advantage by analyzing their strengths, understanding customer needs, and evaluating market trends. A strong advantage often comes from unique products, superior customer service, cost efficiency, or innovative business models that differentiate them from competitors.
What role does goal-setting play in business strategy?
Goal-setting provides a structured approach to achieving success by defining clear, measurable objectives. It helps businesses stay focused, track progress, and make data-driven decisions. Well-defined goals also align teams and resources towards common priorities, improving overall efficiency.
How does market analysis impact business strategy?
Market analysis helps businesses understand customer behavior, industry trends, and competitor actions. By gathering relevant data, companies can make informed strategic decisions, identify growth opportunities, and mitigate risks, ensuring that their strategy aligns with real market demands.
What are the key components of an effective business strategy?
An effective business strategy includes a clear vision, well-defined goals, competitive analysis, resource allocation, and an execution plan. It also incorporates flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions while ensuring that all business functions work toward a common objective.
Further reading
Vistage. “10 Steps to Building the Best Business Strategies.” Vistage, November 5, 2018. https://www.vistage.com/research-center/business-leadership/strategic-planning/20181105-10-steps-building-best-business-strategies/. (Accessed March 7, 2025).
Cascade. “The 5 Best Business Strategies I’ve Ever Seen.” Cascade Blog, November 15, 2023. https://www.cascade.app/blog/the-5-best-business-strategies-ive-ever-seen. (Accessed March 7, 2025).
WebFX. “What Is Business Strategy? Definition, Components, and Examples.” WebFX Blog, January 12, 2024. https://www.webfx.com/blog/marketing/business-strategy/. (Accessed March 7, 2025).
Harvard Business Review. “How to Develop a Business Strategy.” YouTube video, 10:32. Uploaded October 15, 2023. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QZs-IS4yhOU. (Accessed March 7, 2025).
TEDx Talks. “The Secret to Strategic Implementation: Business Strategy Explained.” YouTube video, 14:10. Uploaded March 21, 2022. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c0qnOmNn9k0. (Accessed March 7, 2025).
HubSpot. “The Most Successful Business Strategies Ever.” YouTube video, 12:05. Uploaded September 5, 2021. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KAKyHYkdQ8I. (Accessed March 7, 2025).